Schedule a Visit
Regardless of whether you require general advice or specific support, we are happy to help you.
Regardless of whether you require general advice or specific support, we are happy to help you.
All News
Share
Should you invest in a 3-axis or 5-axis CNC machine? The answer depends on your part complexity, tolerances, and budget. A 3-axis CNC (investment: $50K–$150K) excels at prismatic parts with ±0.01–0.02mm accuracy, while a 5-axis machine ($150K–$500K+) achieves ±0.003mm tolerances and handles freeform geometries in a single setup—cutting cycle times by up to 65%. In this 2026 guide, OPMT Laser’s engineering team (200+ installations across aerospace, medical, and automotive sectors) breaks down the key differences, cost-benefit analysis, and how to match the right machine to your production needs.
3-axis CNC machining is a computer-controlled subtractive manufacturing process where the cutting tool moves along three linear axes: X (left–right), Y (front–back), and Z (up–down). The workpiece stays fixed while the spindle follows programmed toolpaths to remove material, creating prismatic features, pockets, and profiles. With typical positional accuracy of ±0.01–0.02mm and surface roughness of Ra 1.6–3.2 μm, 3-axis machines are widely deployed across automotive, aerospace, electronics, and general manufacturing. According to industry reports, 3-axis systems remain the most cost-effective choice when parts require access from only one or two orientations.
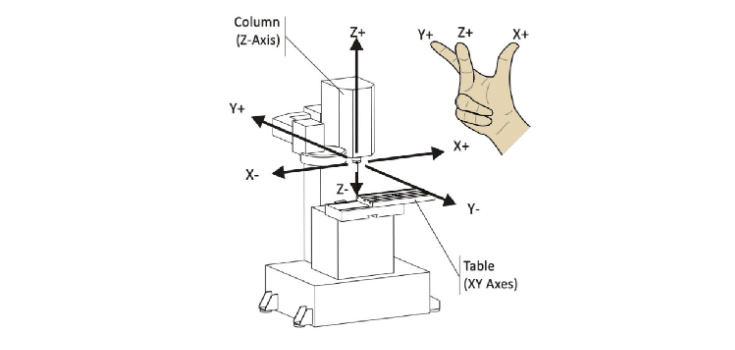
3-axis CNC machining is a precise manufacturing process that creates complex parts through computer-controlled movement along three linear axes. Here’s a concise breakdown of the process:
Digital Design Creation
Machine Code Generation
Workpiece and Tool Setup
Automated Material Removal
Quality Inspection
The CNC machine’s cutting tool moves relative to the stationary workpiece, removing material with high accuracy. This computer-guided process ensures exceptional precision and repeatability, making it ideal for producing intricate components across various industries.
In a modern vertical 3‑axis machining center, typical performance ranges are:
Actual capabilities depend on spindle type, linear guide system, machine rigidity, and process optimization.
3-axis CNC machining delivers exceptional accuracy in part production. The automated process significantly reduces manual labor, minimizing errors and boosting productivity. This precision ensures consistent quality across multiple parts, making it ideal for industries requiring exacting standards.
Compared to more complex CNC systems, 3-axis machines offer a lower initial investment and reduced maintenance costs. This makes them an economical choice for small to medium-sized businesses, allowing for competitive pricing without compromising quality.
3-axis CNC machines excel in working with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites. This versatility enables manufacturers to create diverse products using a single machine, adapting to various industry needs.
The straightforward nature of 3-axis machining makes it easier to program and operate compared to more complex systems. This simplicity reduces setup time and training requirements, allowing for faster project turnaround and increased overall efficiency.
3-axis machining is particularly well-suited for creating flat or slightly curved surfaces, making it perfect for components like brackets, gears, and control panels. Industries such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics benefit from its ability to produce precise, functional parts.
By 2025, advancements in 3-axis CNC technology are expected to further enhance these advantages, with improved spindle technology and control systems leading to even higher levels of precision and efficiency.
3-axis CNC machining is widely used across multiple industries for producing precision components. Here are the main applications:
Each industry benefits from the precision, repeatability, and efficiency of 3-axis CNC machining, enabling the production of complex parts with tight tolerances.
| Industry | Common Applications | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Engine blocks, cylinder heads | High precision, mass production |
| Aerospace | Wing components, fuselage parts | Lightweight materials, complex geometries |
| Medical | Orthopedic implants, dental devices | Biocompatible materials, customization |
| Electronics | Smartphone casings, circuit boards | Fine details, high volume production |
| Manufacturing | Injection molds, stamping dies | Durability, complex tooling |
| Prototyping | Concept models, functional prototypes | Quick turnaround, design iteration |
While 3‑axis CNC machining is highly versatile, it has clear boundaries engineers should recognise:
To maximise the efficiency and stability of 3‑axis CNC processes:
5-axis CNC machining is an advanced manufacturing technique that enables simultaneous movement across five axes:
This configuration allows operators to approach a workpiece from virtually any angle in a single setup, eliminating manual repositioning and reducing setup time by up to 65%. Premium 5-axis machines achieve positioning accuracy within ±0.003mm and support complex freeform geometries—making them essential for aerospace turbine blades, medical implants, and precision mold tooling.
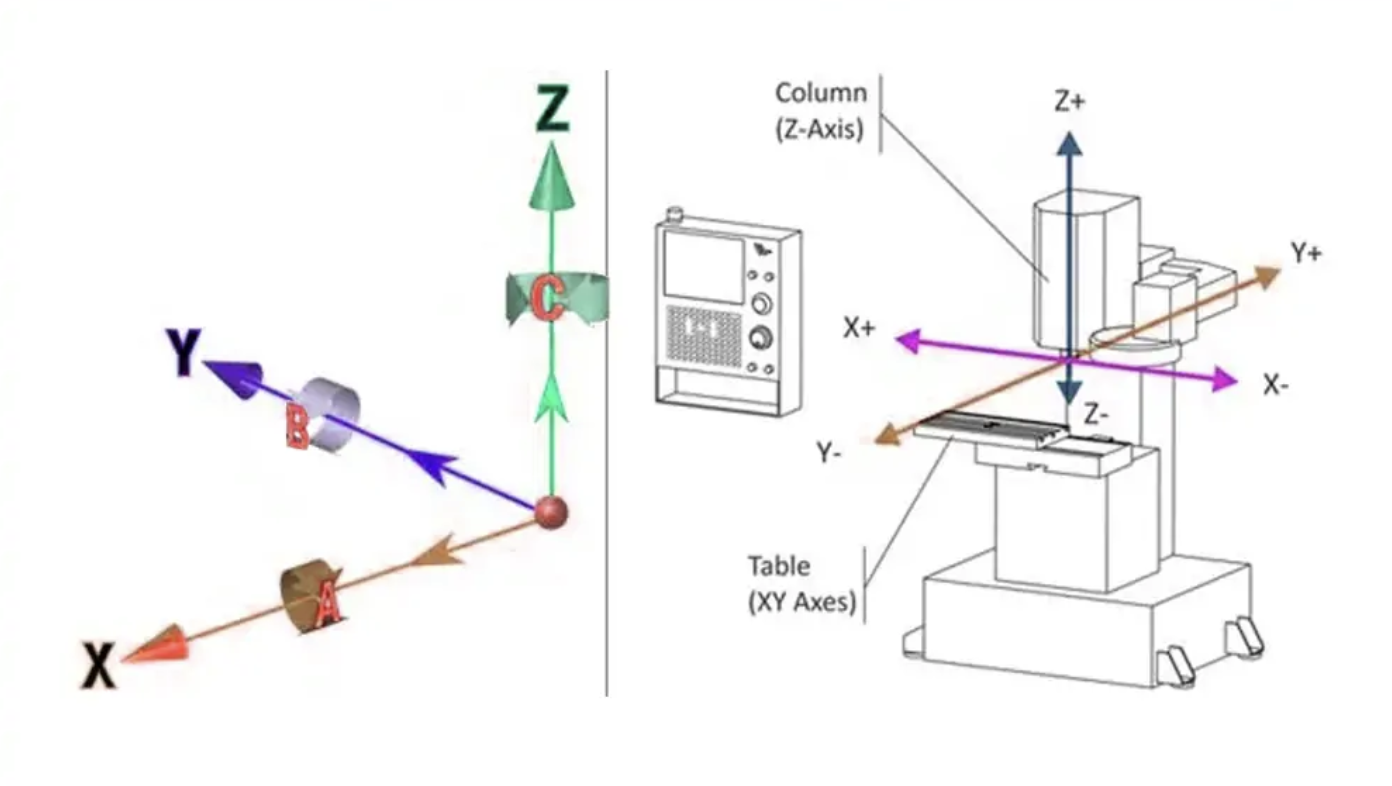
5‑axis CNC machining extends the capabilities of 3‑axis systems in several critical dimensions:

In continuous 5-axis machining, the cutting tool and workpiece move simultaneously along all five axes. This approach:
Also known as indexed 5-axis machining, this method:
5-axis CNC machining is crucial in several high-precision industries:
To maximize the benefits of 5-axis machining:
By leveraging these advanced capabilities, manufacturers can stay competitive in industries demanding high-precision, complex parts with shorter lead times.
CNC machining has revolutionized manufacturing, offering precision and efficiency across industries. But how do 3-axis and 5-axis CNC machines compare? Let’s explore their unique capabilities and ideal use cases.
3-axis CNC machines operate along the X, Y, and Z axes, allowing for linear movement in three directions. This configuration is well-suited for creating parts with flat surfaces and simple geometries. In contrast, 5-axis machines add two rotational axes (A and B) to the mix, enabling the cutting tool to approach the workpiece from multiple angles.
While 3-axis machines excel at simpler cuts, 5-axis CNC machining offers superior efficiency for complex parts. How does this translate to real-world applications? Consider aerospace components:
5-axis machines can complete intricate parts in a single setup, reducing production time and improving accuracy.
Cost reality check: 3-axis CNC machines typically range from $50,000–$150,000, while 5-axis systems start around $150,000 and can exceed $500,000 for high-end configurations. However, the true cost comparison isn’t just about purchase price—it’s about total cost of ownership (TCO).
| Factor | 3-Axis Machining | 5-Axis Machining |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Capex Range | Lower initial investment; suitable for small to mid-size shops | Higher initial investment; justified when complex work is frequent |
| Lifecycle Cost Drivers | More fixtures, more setups, higher operator time on complex parts | Higher programming complexity but fewer fixtures and setups per part |
| Suitable Annual Volume | Efficient for low to medium complexity parts at small to large volumes | Best ROI when a significant portion of throughput involves complex multi-face parts |
| Typical Part Complexity | Simple to moderate geometries, limited undercuts, accessible from 1–2 orientations | Highly complex geometries, deep cavities, multiple compound angles, critical surfaces |
| Setup Time | Longer and more frequent for multi-face parts due to reclamping | Shorter overall for complex parts thanks to single-setup machining |
When does 5-axis pay off? If more than 50% of your part portfolio requires:
…then a 5-axis platform typically delivers better TCO within 2–3 years, thanks to reduced fixtures, fewer setups, and improved first-pass quality. For prismatic parts with simple geometry, a well-optimized 3-axis cell remains highly competitive and often more economical.
Pro tip: Contact OPMT Laser for a personalized cost-benefit analysis based on your specific part mix.
Both 3-axis and 5-axis machines can achieve high precision, but 5-axis machines often excel in creating smooth surface finishes on complex geometries. This is particularly valuable in industries like medical device manufacturing, where implants require exceptional surface quality.
Which industries benefit most from each type of CNC machine?
The choice between 3-axis and 5-axis CNC machining ultimately depends on the complexity of parts, production volume, and budget constraints.
As we look towards 2025, the CNC machining landscape continues to evolve. Key trends include:
These advancements are making both 3-axis and 5-axis CNC machining more efficient and accessible to a wider range of manufacturers.
What is the main difference between 3-axis and 5-axis CNC machining?
The main difference is the number of movement directions: 3-axis machines move along X, Y, and Z linear axes, while 5-axis machines add two rotational axes (typically A and B). This allows 5-axis machines to access complex geometries from multiple angles in a single setup, reducing cycle time by up to 65%.
Is 5-axis CNC machining worth the investment?
Yes, if your production involves complex parts with freeform surfaces, undercuts, or features requiring access from 4+ faces. While 5-axis machines cost 2–3x more upfront ($150K–$500K vs $50K–$150K for 3-axis), they often deliver better total cost of ownership within 2–3 years through reduced setups and higher first-pass quality.
What industries use 5-axis CNC machines?
5-axis CNC machining is essential in aerospace (turbine blades, structural components), medical (implants, surgical instruments), automotive (precision engine parts), and tool & die making. Any application requiring complex geometries and tight tolerances (±0.003mm) benefits from 5-axis capability.
Can 3-axis CNC machines produce complex parts?
3-axis CNC machines can produce moderately complex parts, but with limitations. Parts requiring access to multiple faces need multiple setups, which increases cycle time, datum errors, and scrap risk. For truly complex geometries with undercuts or freeform surfaces, 5-axis machining is more efficient.
Still unsure about choosing between a 5-axis and 3-axis CNC machine for your 2025 projects? OPMT Laser’s expert team can guide you through your CNC machining options, ensuring you select the ideal process for your specific needs. As a leading CNC machining partner, OPMT Laser offers cutting-edge capabilities with advanced router-, lathe-, drill-, and mill-based equipment. Contact OPMT Laser today to elevate your manufacturing precision and efficiency.
Disclaimer
This content is compiled by OPMT Laser based on publicly available information for reference only; mentions of third-party brands and products are for objective comparison and do not imply any commercial association or endorsement.

Explore OPMT’s proven 5-phase ODM process for custom laser systems. ISO-certified manufacturing, ±0.003mm precision, IP protection. Submit project requirements today.

Looking for the best 5-axis CNC machining center suppliers? Check our top 10 list for expert insights and find the perfect fit for your needs!

Explore the top 10 laser metal cutting machines of 2025, featuring industry leaders like Trumpf, Bystronic, and OPMT Laser. Compare cutting-edge technology, precision, and efficiency to find the perfect solution for your manufacturing needs.

Uncover the top 10 laser cutting manufacturers for 2025, featuring trusted brands, competitive pricing, and innovative technology that can transform your production process.
Please fill in your contact information to download the PDF.

