Schedule a Visit
Regardless of whether you require general advice or specific support, we are happy to help you.
Regardless of whether you require general advice or specific support, we are happy to help you.
All News
Share
TL;DR: 5-axis laser cutting systems combine three linear axes (X, Y, Z) with two rotational axes (A, B) to process materials from virtually any angle. This multi-axis configuration enables manufacturers to cut complex 3D geometries, process ultra-hard materials like PCD and ceramics, and achieve positioning accuracies of ±0.005mm without multiple setups—delivering 66% faster cycle times compared to conventional methods.
5 axis laser machines represent the convergence of advanced motion control and ultrafast laser processing technology, enabling manufacturers to machine complex geometries that were previously impossible or economically unviable. As global industries demand tighter tolerances and more intricate component designs—particularly in aerospace turbine blades, medical implants, and EV powertrain tooling—the limitations of traditional 3-axis laser systems have become increasingly apparent. This comprehensive guide examines the technical architecture, competitive advantages, industrial applications, and selection criteria for 5-axis laser cutting equipment, providing manufacturing decision-makers with actionable intelligence for capital equipment investments.
A 5 axis laser cutter integrates three orthogonal linear axes (X, Y, and Z) with two independent rotational axes—typically designated as B-axis (tilt) and C-axis (rotation)—to achieve complete geometric freedom during material processing. This kinematic configuration allows the laser focal point to approach workpieces from virtually unlimited angles while maintaining optimal beam perpendicularity to the cutting surface.
The technical architecture of modern 5 axis laser machines employs linear motors for the translation axes, delivering rapid traverse speeds up to 30 m/min with acceleration capabilities of 2.5 g. Rotational axes utilize high-precision torque motors that provide angular positioning accuracy of 5-10 arcseconds, critical for maintaining beam alignment during simultaneous multi-axis interpolation. Full closed-loop grating scale detection systems continuously monitor actual position versus commanded position, compensating for thermal expansion, mechanical deflection, and servo lag in real-time.
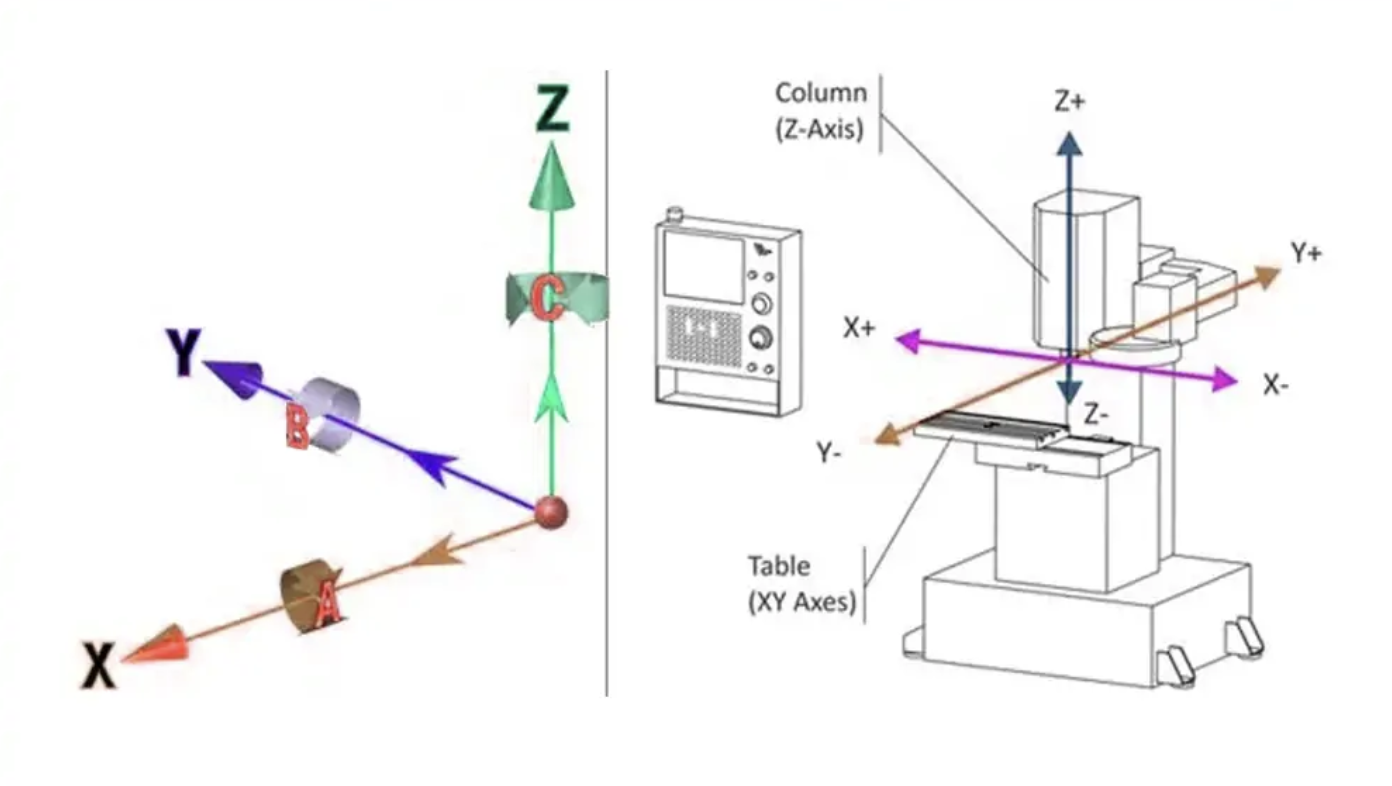
Key technological components include laser galvanometer systems with sub-2 µrad repeat positioning accuracy, enabling precision beam steering for both cutting and rotary drilling applications. Advanced CNC platforms—such as NUM Flexium+ or proprietary OPMT control systems—implement Real-Time Tool Center Point (RTCP) algorithms that calculate instantaneous axis positions to maintain constant focal point location regardless of B and C axis orientation. This computational capability eliminates the need for complex post-processor programming, reducing setup time by 40-60% compared to traditional CAM workflows.
The modular beam path design incorporates CCD positioning cameras and high-precision touch probes that automatically detect workpiece datum points and tool offsets. This sensor integration enables lights-out operation with automatic error correction, particularly valuable for high-mix, low-volume production environments where frequent part changeovers would otherwise consume significant setup labor.
Precision capabilities extend to positioning accuracy of ±0.005mm across all linear axes, with repeat positioning accuracy of ±0.003mm—specifications that enable consistent processing of ultra-hard materials including polycrystalline diamond (PCD), cubic boron nitride (CBN), advanced ceramics, and carbide composites. Femtosecond laser systems operating at pulse widths below 500 femtoseconds minimize heat-affected zones to less than 50 µm, preserving material properties in thermally sensitive applications.
The operational and economic advantages of 5 axis laser cutting versus conventional 3-axis configurations manifest across six critical performance dimensions:
| Performance Metric | 3-Axis Laser Systems | 5-Axis Laser Systems | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Setup Requirements | Multiple fixtures and repositioning operations | Single-clamping complete processing | 60-75% setup time reduction |
| Geometric Capability | Limited to 2.5D profiles and planar surfaces | Full 3D contours, undercuts, and non-planar features | Unlimited angular access |
| Cycle Time (Complex Parts) | 120-180 minutes (automotive tooling) | 40-60 minutes (same component) | 66-200% faster throughput |
| Energy Consumption | 8.0 kWh per part (EDM equivalent) | 4.5 kWh per part (ultrafast laser) | 44% energy savings |
| Operational Cost | $4,190/month (including consumables) | $1,956/month (no electrode wear) | 53% cost reduction |
| Surface Finish | Ra 0.8-1.2 µm (requiring secondary operations) | Ra 0.4-0.6 µm (single-pass completion) | 40% roughness improvement |
Setup reduction represents the most immediate operational benefit. Traditional 3-axis laser systems require multiple fixture reorientations to access different part faces, with each repositioning introducing cumulative geometric error and consuming 15-30 minutes per setup. Five-axis configurations complete complex parts—such as PCD flooring cutters with teeth, flank, and relief surfaces—in a single clamping operation, eliminating error stacking and reducing touch time by 60-75%.
Geometric capability expands dramatically with rotational axis integration. While 3-axis systems excel at cutting planar sheets and simple extrusions, they cannot process deep contours, internal undercuts, or continuously varying surface geometries without dedicated fixturing. Five-axis machines machine turbine blade cooling passages, medical implant screw threads, and cutting tool chip breakers that would be geometrically impossible with triaxial motion alone.
Cycle time improvements of 66-200% have been documented for complex automotive tooling applications, where traditional EDM processes consuming 120-180 minutes per component are reduced to 40-60 minutes through continuous multi-axis laser machining. This throughput advantage compounds in high-volume production, generating ROI acceleration of 18-24 months versus conventional technology.
Energy efficiency gains stem from eliminating thermal processing consumables. Femtosecond laser systems consume 44% less energy than equivalent EDM or grinding operations, with no electrode fabrication, dielectric fluid management, or grinding wheel truing requirements. Monthly operational costs decrease from $4,190 to $1,956 when transitioning from conventional to 5-axis laser manufacturing systems.
Quality enhancement manifests through optimal cutting angle maintenance. By continuously adjusting B and C axes to keep the laser beam perpendicular to instantaneous cutting vectors, five-axis systems minimize taper, reduce kerf width variation, and achieve 40% smoother surface finishes than fixed-angle alternatives.
5 axis laser machine technology has achieved widespread adoption across six industrial sectors demanding ultra-precision component manufacturing:
Automotive Manufacturing: Step-forming milling cutters, brazed tip tools, and micro-edge tooling for electric vehicle powertrain components represent the largest application segment. Five-axis laser systems process PCD-tipped cutting tools that machine aluminum battery housings and motor casings, where conventional grinding would generate excessive heat and compromise diamond-to-carbide braze joints. Complex contour tooling for instrument panel molds and interior trim dies leverage multi-axis capability to machine draft angles and undercuts in single operations.

Aerospace Engineering: Turbine blade manufacturing constitutes 40% of aerospace laser machining applications. Five-axis systems machine single-crystal superalloy blades with internal cooling passages, film cooling holes (0.3-1.0mm diameter), and trailing edge geometry—all features requiring non-orthogonal beam approach angles impossible with 3-axis configurations. Wing spar drilling for composite aircraft structures, landing gear component finishing, and engine mount precision cutting further expand aerospace adoption. Stress-resistant precision requirements—where residual stress must remain below 50 MPa to prevent fatigue crack initiation—demand femtosecond pulse widths that five-axis platforms uniquely deliver.
Medical Device Production: LASIK surgical instrument fabrication, cardiovascular stent cutting, orthopedic implant texturing, and dental prosthetic manufacturing leverage five-axis capability to process biocompatible materials including titanium alloys, cobalt-chromium, and medical-grade ceramics. Sub-50µm heat-affected zone requirements prevent metallurgical changes that could trigger adverse biological responses. Intricate geometries such as spinal cage fusion windows, hip implant taper junctions, and heart valve leaflet profiles require continuous 5-axis interpolation to maintain dimensional tolerances of ±10 µm across complex curved surfaces.
3C Electronics: Precision cutting of multi-layer circuit boards, smartphone chassis machining, camera module housing fabrication, and advanced display technology component production utilize five-axis laser systems to process brittle materials including sapphire, gorilla glass, and silicon carbide without inducing microcracks. The ability to tilt the laser beam reduces edge chipping by 60-80% compared to vertical-only cutting approaches.
Cutting Tool Industry: PCD flooring cutters, CBN grinding wheel profiling, carbide insert geometries, and woodworking saw blade fabrication represent traditional five-axis laser applications. Processing ultra-hard materials with hardness values exceeding 70 HRC requires femtosecond pulse widths and multi-axis motion to maintain optimal ablation efficiency while minimizing thermal damage to substrate materials.
Material Compatibility spans ultra-hard materials (PCD, CBN), advanced ceramics (silicon nitride, alumina, zirconia), high-strength alloys (Inconel, titanium-aluminum-vanadium), composite materials (carbon fiber reinforced polymers), and thin-walled metal parts requiring sub-0.5mm wall thickness maintenance without thermal distortion.
Manufacturing engineers evaluating 5 axis laser cutting machines should assess seven critical specification categories:
| Specification Category | Entry-Level Systems | Production Systems | Premium Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| X-Axis Travel | 250-400mm | 400-600mm | 600-800mm |
| Y-Axis Travel | 200-250mm | 250-350mm | 350-500mm |
| Z-Axis Travel | 200-300mm | 300-400mm | 400-600mm |
| B-Axis Range | -30° to +90° | -110° to +120° | ±120° continuous |
| C-Axis Rotation | 360° indexed | 360° continuous | Unlimited continuous |
| Positioning Accuracy (Linear) | ±0.008mm | ±0.005mm | ±0.003mm |
| Angular Positioning | ±10 arcsec | ±5 arcsec | ±2 arcsec |
| Rapid Traverse Speed | 20 m/min | 30 m/min | 40 m/min |
| Laser Power Range | 50-200W | 100-500W | 500-1000W+ |
| Workpiece Load Capacity | 10-50kg | 50-200kg | 200-500kg |
Axis Configuration directly impacts accessible work envelope and geometric flexibility. X-axis travel of 400-600mm accommodates standard cutting tool diameters up to 200mm, while Y-axis travel of 250mm provides adequate clearance for rotary axis swing. Z-axis travel of 300-400mm enables deep cavity machining without collision risk. B-axis swing angles of ±110° to +120° allow near-complete hemispherical access, critical for machining conical tool forms and turbine blade airfoils. C-axis 360° continuous rotation enables helical interpolation for thread cutting and spiral groove machining.
Laser Parameters determine material processing capability and throughput. Pulse width selection—femtosecond (10-500 fs), picosecond (1-50 ps), or nanosecond (1-100 ns)—governs heat-affected zone dimensions and material removal mechanisms. Femtosecond systems minimize thermal damage for ultra-hard materials and medical devices, while nanosecond pulses provide higher material removal rates for high-volume production. Power ranges of 100-500W balance precision and productivity, with higher power enabling faster cutting speeds but requiring more sophisticated thermal management. Wavelength compatibility (1064nm infrared, 532nm green, 355nm UV) expands material processing versatility, particularly for transparent materials and polymer composites.
Accuracy Metrics define dimensional capability. Positioning accuracy of ±0.005mm represents the maximum deviation from commanded position, directly impacting finished part tolerance capability. Repeat positioning accuracy of ±0.003mm determines process consistency across production batches. Angular positioning accuracy of 5-10 arcseconds translates to ±25-50 µm positional error at 100mm radius—a critical consideration for cutting tool geometry where angular errors compound into significant dimensional deviations.
Speed Capabilities impact cycle time and throughput. Cutting speeds of 10-20 m/min establish material removal rates, while rapid traverse speeds of 30-40 m/min minimize non-productive repositioning time. Rotary axis speeds of 100-300 rpm enable efficient indexing between cutting operations without sacrificing settling time for high-frequency servo control loops.
Workpiece Capacity specifications include horizontal workbench dimensions (typically 500×500mm for mid-range systems), load capacity (10-300kg depending on application), and maximum tool diameter/length constraints that prevent collision during multi-axis motion. Threaded hole patterns on worktables enable modular fixturing for diverse component geometries.
Control Systems integrate CNC platforms (NUM, NEWCON, Siemens 840D) with specialized CAM software. Proprietary post-processors for OPMT-specific control architectures optimize toolpath generation for simultaneous 5-axis interpolation, while probe detection systems enable automatic workpiece alignment and tool offset measurement for lights-out manufacturing.
Manufacturing executives evaluating capital equipment investments should assess seven critical decision factors when selecting 5 axis laser machine suppliers:
Manufacturer Credentials: Verify ISO certifications (9001 quality management, 14001 environmental, 45001 occupational health) that demonstrate systematic quality processes. Review patent portfolios related to ultrafast laser processing, multi-axis kinematics, and thermal management—indicators of sustained R&D investment. Established manufacturers typically allocate 15-25% of annual revenue to technology development, ensuring long-term platform evolution and spare parts availability.
Machine Architecture: Evaluate bed construction materials—marble versus welded steel—for thermal stability characteristics. Natural granite exhibits thermal expansion coefficients 40% lower than steel, maintaining micron-level positioning accuracy across 20°C temperature swings typical in production environments. Linear motor drive systems eliminate backlash and mechanical wear inherent in ball screw transmissions, reducing maintenance intervals by 60% while improving dynamic response. Torque motor rotary axes provide superior angular positioning compared to worm gear indexers, particularly for simultaneous 5-axis contouring.
Integration Capabilities: Assess compatibility with existing CAM software ecosystems (Mastercam, Siemens NX, CATIA) through standardized post-processor libraries. Evaluate training program depth—comprehensive operators, programmers, and maintenance technicians require 40-80 hours of structured instruction for proficiency. Software customization options for industry-specific applications (dental implant libraries, cutting tool templates, aerospace part families) accelerate time-to-production by 30-50%.
Service Infrastructure: Confirm regional support availability within your operating geography, with response time guarantees of 24 hours (critical production equipment) or 48 hours (backup capacity). Verify spare parts inventory locations—overnight delivery capability prevents extended downtime from component failures. Preventive maintenance programs with 6-month inspection intervals ensure positioning accuracy retention and extend mechanical component service life.
Application Validation: Request case studies from manufacturers serving your target industry, with documented cycle times, quality metrics, and ROI timelines. Trial machining services enable process validation before capital commitment—provide representative workpiece geometry and material specifications to generate empirical cutting parameters. Obtain complete process parameter documentation including laser power profiles, feed rates, assist gas pressures, and focal point offsets for initial production ramp-up.
Total Cost of Ownership: Initial capital investment for production-grade systems ranges from $300,000 to over $1,000,000 depending on configuration. Calculate operational energy costs using documented 44% savings potential versus conventional thermal processing. Factor tooling elimination benefits—no electrode fabrication, grinding wheels, or cutting tool inventory—that reduce consumable expenses by 50-60%. Include facility infrastructure requirements: electrical service (380V three-phase, 25-35 kVA), compressed air supply (0.7 MPa, 500 L/min), and environmental controls (±2°C temperature stability for ultra-precision applications).
Leading Suppliers include OPMT Laser with Light 5X series (40V and 60V vertical configurations) and LP550V ultrafast rotary cutting platforms, alongside international manufacturers BLM GROUP (LT-FREE systems), Trumpf (TruLaser series), and Prima Power (5-axis tube laser systems). Regional availability, industry-specific application engineering, and lifecycle support capabilities differentiate supplier value propositions beyond base machine specifications.
5 axis laser machines have transitioned from specialized research platforms to production-critical manufacturing assets across aerospace, medical device, automotive, and cutting tool industries. The combination of multi-axis geometric freedom, femtosecond pulse precision, and closed-loop positioning accuracy enables manufacturers to process ultra-hard materials and complex geometries previously limited by conventional technology constraints. Documented advantages—including 66% cycle time reduction, 44% energy savings, and 53% operational cost improvement—deliver compelling ROI for capital equipment investments.
Manufacturing decision-makers should prioritize application validation through trial machining services, verify supplier service infrastructure for long-term support, and conduct comprehensive TCO analysis incorporating energy, consumables, and setup labor savings. For manufacturers requiring integrated mechanical and laser processing capabilities, advanced 5-axis CNC machining centers offer comprehensive solutions beyond laser-only systems, combining milling, turning, and multi-axis laser technologies in unified platforms that maximize equipment utilization and minimize work-in-process inventory.
As global manufacturing continues its trajectory toward mass customization and precision component miniaturization, five-axis laser cutting systems represent essential enabling technology for competitive participation in high-value industrial sectors. Evaluate your specific application requirements against the technical specifications and supplier selection criteria outlined in this guide to identify optimal equipment configurations for your manufacturing objectives.
Disclaimer
This content is compiled by OPMT Laser based on publicly available information for reference only; mentions of third-party brands and products are for objective comparison and do not imply any commercial association or endorsement.
Explore the world of CNC machining as we compare 3-axis and 5-axis technologies. From basic operations to complex geometries, find out which machine suits your manufacturing needs in 2025.

Explore OPMT’s proven 5-phase ODM process for custom laser systems. ISO-certified manufacturing, ±0.003mm precision, IP protection. Submit project requirements today.

Looking for the best 5-axis CNC machining center suppliers? Check our top 10 list for expert insights and find the perfect fit for your needs!

Explore the top 10 laser metal cutting machines of 2025, featuring industry leaders like Trumpf, Bystronic, and OPMT Laser. Compare cutting-edge technology, precision, and efficiency to find the perfect solution for your manufacturing needs.
Please fill in your contact information to download the PDF.

