Schedule a Visit
Regardless of whether you require general advice or specific support, we are happy to help you.
Regardless of whether you require general advice or specific support, we are happy to help you.
All News
Share
TL;DR: A 5-axis laser engraving machine combines three linear axes (X, Y, Z) with two rotational axes (typically B and C) to engrave, mark, or texture complex 3D surfaces with positioning accuracy of ±3-10μm. These systems enable perpendicular beam incidence across compound geometries, allowing precision marking on curved surfaces, cutting tool edges, mold textures, and medical device components that conventional 2-axis or 3-axis laser systems cannot process effectively.
Manufacturing industries requiring permanent identification, traceability marking, and functional surface modification face a critical challenge: how to apply precision engravings to complex three-dimensional geometries without compromising accuracy or damaging delicate components. Traditional laser marking systems operating on two or three axes struggle with non-planar surfaces, requiring multiple setups and introducing positioning errors. 5 axis laser engravers eliminate these limitations by maintaining optimal beam orientation regardless of part geometry, delivering micron-level precision across compound curves, relief angles, and irregular contours. This capability proves essential for applications ranging from medical device UDI marking to aerospace turbine blade identification and precision mold texturing.
Five-axis laser engraving systems integrate synchronized motion control across three linear axes (X, Y, Z) and two rotational axes (typically B-axis tilt and C-axis rotation) to maintain perpendicular laser beam incidence on complex workpiece geometries. This kinematic configuration achieves positioning accuracy of ±3μm to ±10μm with repeatability of ±3μm to ±5μm—specifications unattainable with conventional fixed-orientation laser markers.
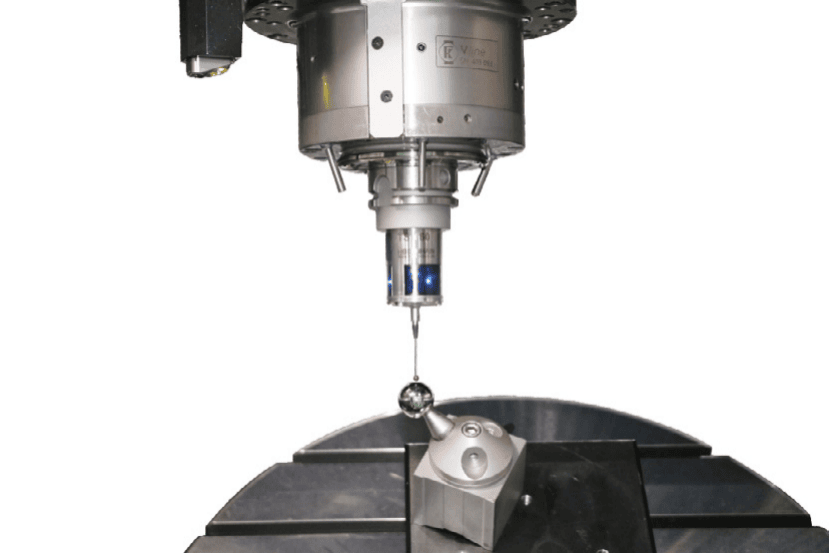

The technical foundation relies on Real-Time Tool Center Point (RTCP) control, which continuously adjusts all five axes to compensate for rotational movements while maintaining constant focal distance between the laser optics and workpiece surface. This dynamic positioning prevents focal point drift that would otherwise degrade mark quality on angled or curved surfaces. Advanced 5 axis laser machines incorporate closed-loop grating scale feedback on all axes, ensuring positional accuracy remains within specification throughout extended production runs.
Laser source integration distinguishes modern 5-axis engraving platforms. Femtosecond lasers (pulse width <500 femtoseconds) enable cold ablation of materials with thermal affected zones below 1μm, critical for marking heat-sensitive medical implants and semiconductor components. Nanosecond fiber lasers (20-200ns pulse width) provide higher average power for rapid marking on metals and ceramics. Picosecond systems bridge these capabilities, offering sub-micron precision with moderate processing speeds suitable for high-volume production.
The rotational workspace defines system versatility. A continuous 360° C-axis combined with a ±110° to ±120° B-axis tilt range provides hemispherical accessibility, allowing complete surface coverage on cylindrical, conical, and spherical workpieces in a single setup. Working envelopes typically span 400-600mm (X) × 250-350mm (Y) × 300mm (Z), accommodating components from miniature medical devices to large automotive molds. For specialized applications like mold texturing, extended C-axis tables up to 600×350mm enable processing of multi-cavity injection molds without repositioning.
Five-axis laser engraving technology addresses critical identification, traceability, and functional surface modification requirements across precision manufacturing sectors:
Cutting Tool Marking: Manufacturers of PCD (polycrystalline diamond) and CBN (cubic boron nitride) cutting tools require permanent serial codes, 2D Data Matrix symbols, and quality control markings positioned within 0.5mm of ultra-hard cutting edges. Five-axis systems process these engravings with edge-proximity precision impossible for 3-axis platforms, enabling full traceability without compromising tool geometry. Character heights as small as 0.3mm maintain legibility under industrial inspection systems while minimizing marked surface area. Laser processing equipment integrating cutting and marking operations eliminates transfer between machines, reducing handling damage risk.

Medical Device Identification: Regulatory compliance mandates Unique Device Identification (UDI) codes on surgical instruments, orthopedic implants, and Class III medical devices. Five-axis laser engravers apply permanent marks to curved implant surfaces, cannulated instrument bores, and ceramic component geometries that conventional marking methods cannot access. Typical specifications include:
Mold Surface Texturing: Injection mold manufacturers apply decorative and functional textures to cavity surfaces, transferring patterns to molded plastic parts. Five-axis laser texturing achieves 0.01mm accuracy across complex mold geometries, creating leather grain patterns, geometric microstructures, and anti-slip surfaces. Systems like the Micro3D L570V process 30-50 texture layers with automatic path planning, eliminating chemical etching processes that produce environmental waste. Applications span automotive interior panels, consumer electronics housings, and luxury goods with intricate surface finishes.
Aerospace Component Marking: Turbine blade traceability requires part numbers, heat lot codes, and inspection stamps on compound-curved airfoil surfaces. Five-axis laser systems maintain perpendicular beam incidence across leading edges, trailing edges, and pressure surfaces, producing high-contrast marks without thermal distortion. Processing parameters adjust automatically based on material (Inconel, titanium alloys, ceramic matrix composites) and surface geometry, ensuring consistent mark depth and clarity across mixed-material assemblies.
The kinematic capabilities of five-axis laser engraving systems deliver measurable productivity and quality improvements compared to conventional three-axis platforms:
Single-Setup Processing Efficiency: Complex components requiring markings on multiple surfaces typically demand 3-5 repositioning operations on 3-axis systems, with each reorientation introducing cumulative positional error. Five-axis platforms complete all marking operations in one setup, reducing cycle time by 30-50% for multi-surface parts while eliminating fixture-induced positioning variations. For high-mix, low-volume production environments—common in aerospace and medical manufacturing—setup time savings compound across part families.
Perpendicular Beam Incidence Quality: Laser beam energy absorption depends critically on incidence angle relative to the target surface. When 3-axis systems attempt to mark angled or curved surfaces, oblique beam angles reduce effective energy density and create asymmetric heat-affected zones. Five-axis RTCP control maintains perpendicular beam orientation regardless of surface geometry, producing uniform mark depth, consistent contrast, and symmetrical heat-affected zones across complex contours. This geometric optimization proves essential for high-resolution 2D barcodes where off-angle marking degrades scanner readability.
Compound Surface Accessibility: Components featuring relief angles, undercuts, and spherical sections challenge fixed-orientation laser systems. Medical bone screws with helical threads, turbine blades with twisted airfoils, and injection molds with draft angles all require variable beam approach angles. Five-axis kinematics position the laser focus path relative to local surface normals, processing features that would require custom fixturing or remain inaccessible on 3-axis platforms. This capability extends to 5 axis laser cutting applications where through-holes must maintain perpendicularity to curved or angled surfaces.
Integrated Machining Workflows: When combined with CNC machining capabilities, five-axis laser systems enable hybrid manufacturing sequences. A typical workflow machines a component geometry, applies precision engravings, then performs finish operations—all within a single work envelope. This integration eliminates work-in-process inventory, reduces handling-induced damage, and ensures dimensional correlation between machined features and applied markings. Contract manufacturers processing small-batch, high-value components realize significant operational efficiency gains from these consolidated workflows.
Five-axis laser engraving systems accommodate diverse material classes through appropriate laser source selection and parameter optimization:
Superhard Materials Processing: PCD cutting tools, CBN grinding wheels, and CVD diamond wear components require femtosecond laser processing to prevent microcracking. Pulse widths below 500fs enable cold ablation, removing material through photomechanical rather than photothermal mechanisms. Typical processing parameters include:
Metal Engraving Applications: Stainless steel, titanium alloys, aluminum, tool steel, and tungsten carbide respond effectively to nanosecond or picosecond fiber lasers. Surface oxidation produces high-contrast black markings on stainless steel without material removal, while ablation-mode processing creates recessed engravings in hardened tool steels. Average laser powers of 20-100W support production marking speeds of 1000-3000mm/s for alphanumeric characters and serialization codes.
Technical Ceramic and Composite Materials: Silicon carbide, zirconia, alumina ceramics, graphite, and carbon fiber composites require wavelength and pulse duration tuning to prevent subsurface damage. Green wavelength lasers (515-532nm) improve absorption in transparent or translucent ceramics, while ultrashort pulse durations minimize heat-affected zones in thermally sensitive composites. Medical ceramic components demand surface roughness maintenance below 0.8μm Ra after marking to prevent biofilm formation.
Standard Processing Specifications: Industrial five-axis laser engraving systems typically offer:
These specifications enable processing of components ranging from miniature medical implants to large automotive molds within validated quality control tolerances.
OPMT’s portfolio of five-axis laser engraving platforms addresses diverse industrial marking, texturing, and micro-machining requirements through specialized system configurations:

Light 5X Series (40V/60V Models): These vertical 5-axis laser machining centers integrate engraving, cutting, and texturing capabilities within unified platforms designed for PCD/CBN cutting tool production and automotive component processing. The Light 5X 40V features a 400mm × 250mm × 300mm working envelope with HSK-E40 spindle interface, supporting combination laser-mechanical workflows. The 60V extends X-axis travel to 600mm for larger automotive tooling. Both platforms achieve ±3μm repeat positioning accuracy through linear motor drives on all three linear axes and torque motor actuation of B/C rotary axes. Closed-loop grating scale feedback maintains positional accuracy throughout thermal cycling and extended production runs. Self-developed CNC systems provide integrated CAM functionality for laser technology applications spanning marking, texturing, and precision cutting.
Micro3D L530V Femtosecond System: Engineered for ultra-precision marking and micro-nano structuring, the L530V integrates femtosecond laser sources with five-axis kinematics to process 3D complex structures on superhard materials. The system achieves ±10μm positioning accuracy across a work envelope suitable for cutting tool inserts, medical micro-components, and semiconductor devices. Femtosecond pulse widths below 500fs enable cold ablation of PCD, CBN, and ceramic materials without heat-affected zone formation, critical for maintaining edge sharpness on cutting tools and preventing microcrack propagation in brittle materials. Optional galvanometer scanning heads accelerate high-density pattern generation for micro-texturing applications.
Micro3D L570V Mold Texturing Specialist: Purpose-designed for injection mold surface texturing, the L570V combines 5-axis mechanical positioning with 3D texture simulation and automatic path planning software. The system processes texture patterns up to 30-50 layers deep with 0.01mm accuracy, creating decorative leather grains, functional anti-slip surfaces, and geometric microstructures across complex mold cavities. Intelligent software automatically partitions large texture areas into processing blocks, generates collision-free toolpaths, and optimizes laser parameters for consistent depth control. Compatibility with both nanosecond and femtosecond laser sources enables processing of tool steels, aluminum molds, and specialty alloys within a single platform. The extended C-axis rotary table (up to 600×350mm) accommodates multi-cavity automotive and consumer goods molds, eliminating chemical etching processes that generate hazardous waste streams.
Integrated CNC Control Systems: All OPMT five-axis laser platforms incorporate proprietary CNC systems featuring collision detection, real-time motion simulation, and CAD/CAM integration. The texturing-specific software offers 3D model import, automatic texture pattern generation from grayscale images, and intelligent layer decomposition for multi-pass depth control. For production environments, the systems support barcode-triggered parameter selection, statistical process control data logging, and Industry 4.0 connectivity for manufacturing execution system integration. These software capabilities differentiate OPMT platforms as turnkey solutions rather than requiring third-party CAM programming or offline path planning tools.
Five-axis laser engraving machines deliver precision marking, identification, and surface modification capabilities essential for industries where component traceability, regulatory compliance, and functional surface properties directly impact product performance and safety. The kinematic flexibility to maintain perpendicular beam incidence across complex three-dimensional geometries—combined with positioning accuracies of ±3μm to ±10μm—enables applications ranging from medical device UDI marking to aerospace component serialization and precision mold texturing.
Manufacturers evaluating 5-axis laser engraving systems should prioritize three key specifications: positioning accuracy aligned with mark resolution requirements, rotational workspace sufficient for part geometry complexity, and laser source compatibility with target materials. For high-mix production environments processing diverse part families, the single-setup efficiency of five-axis platforms delivers 30-50% cycle time reductions while eliminating multi-operation positioning errors.
OPMT’s specialized platforms—from the Light 5X series for integrated cutting-marking workflows to the Micro3D L570V for complex mold texturing—provide industrial manufacturers with validated solutions backed by self-developed CNC systems and application engineering support. As regulatory requirements for permanent part identification expand and functional surface modification techniques advance, five-axis laser engraving technology will increasingly define competitive capabilities in precision manufacturing sectors.
For comprehensive guidance on integrating laser processing into multi-axis CNC environments, explore best practices for laser CNC machining centers and discover how hybrid manufacturing platforms optimize production workflows across cutting, marking, and finishing operations.
Disclaimer
This content is compiled by OPMT Laser based on publicly available information for reference only; mentions of third-party brands and products are for objective comparison and do not imply any commercial association or endorsement.

Explore the world of CNC machining as we compare 3-axis and 5-axis technologies. From basic operations to complex geometries, find out which machine suits your manufacturing needs in 2025.

Explore OPMT’s proven 5-phase ODM process for custom laser systems. ISO-certified manufacturing, ±0.003mm precision, IP protection. Submit project requirements today.

Looking for the best 5-axis CNC machining center suppliers? Check our top 10 list for expert insights and find the perfect fit for your needs!

Explore the top 10 laser metal cutting machines of 2025, featuring industry leaders like Trumpf, Bystronic, and OPMT Laser. Compare cutting-edge technology, precision, and efficiency to find the perfect solution for your manufacturing needs.
Please fill in your contact information to download the PDF.

