Vereinbaren Sie einen Besuch
Egal ob Sie eine allgemeine Beratung oder spezifische Unterstützung benötigen, wir helfen Ihnen gerne weiter.
Egal ob Sie eine allgemeine Beratung oder spezifische Unterstützung benötigen, wir helfen Ihnen gerne weiter.
Alle News
Aktie
Die Fertigung von Präzisionsbohrvorgängen hat einen entscheidenden Wendepunkt erreicht. Traditionelle 3-Achs-Bohrsysteme stoßen an geometrische Grenzen, die zu kostspieligen Mehraufspannungen, akkumulierten Toleranzfehlern und einer beeinträchtigten Positioniergenauigkeit führen. 5-Achs-CNC-Bearbeitungszentren für das Bohren beseitigen diese grundlegenden Einschränkungen durch simultane Mehrachsen-Bewegungssteuerung und ermöglichen so Bohrungen mit komplexen Winkeln, die Positioniergenauigkeiten von ±0,005 mm erreichen und gleichzeitig die Zykluszeiten um 40–701 TP3T reduzieren.
Diese hochentwickelten Bearbeitungssysteme integrieren drei Linearachsen (X, Y, Z) mit zwei Rotationsachsen (typischerweise B und C) und ermöglichen so vollständige geometrische Freiheit beim Bohren. Die technischen Vorteile gehen über die Winkelzugänglichkeit hinaus: Hersteller erzielen messbare Verbesserungen bei der Bohrungsqualität, der Oberflächengüte und dem Produktionsdurchsatz bei der Bearbeitung komplexer Bauteile in der Luft- und Raumfahrt, der Medizintechnik, der Automobilindustrie und der Werkzeugindustrie.
Dieser umfassende technische Leitfaden untersucht die Einsatzmöglichkeiten, Leistungsspezifikationen und Implementierungsaspekte von 5-Achs-Bohrsystemen. Fertigungsingenieure und Produktionsleiter, die Präzisionsbohrlösungen evaluieren, erhalten wertvolle Einblicke in Systemauswahlkriterien, anwendungsspezifische Konfigurationen und messbare Kennzahlen zur Rentabilität, die Investitionsentscheidungen in Hochpräzisionsbohrumgebungen rechtfertigen.
Fünf-Achs-Bearbeitungszentren für Bohrarbeiten sind hochentwickelte Fertigungsplattformen, die für die Durchführung komplexer Bohrvorgänge in mehreren Ebenen ohne Werkstückumpositionierung konzipiert sind. Diese Systeme koordinieren die simultane Bewegung entlang dreier linearer und zweier rotatorischer Achsen, wodurch das Schneidwerkzeug oder der Laserkopf das Werkstück aus nahezu jedem Winkel innerhalb des Arbeitsbereichs der Maschine anfahren kann.
Die grundlegende Architektur unterscheidet 5-Achs-Bohrzentren von herkömmlichen Anlagen. Linearachsen ermöglichen die Positionssteuerung entlang der X- (horizontalen), Y- (Tiefen-) und Z-Achse (vertikalen) Richtung, während Rotationsachsen – die B-Achse (Neigebewegung) und die C-Achse (Drehbewegung) – das Werkstück bzw. den Werkzeugkopf in präzise Winkelpositionen ausrichten. Diese kinematische Anordnung beseitigt die geometrischen Einschränkungen von 3-Achs-Konfigurationen, bei denen der Bohrer senkrecht zur Werkstückauflagefläche steht.
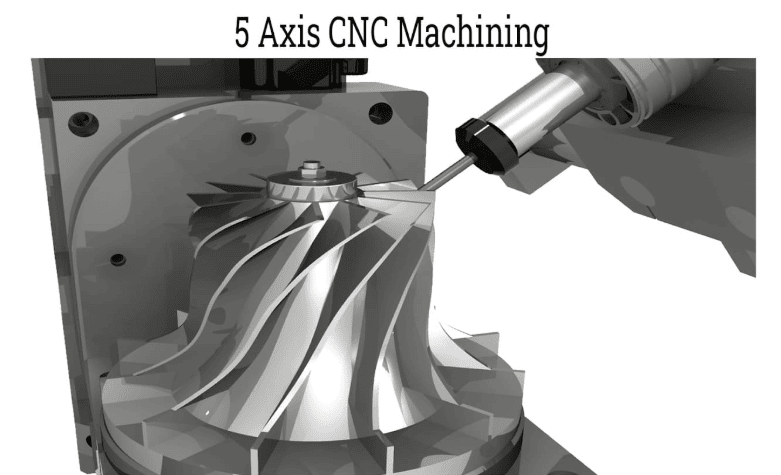
Wesentliche operative Vorteile unterscheiden das 5-Achs-Bohren von herkömmlichen Verfahren. Hersteller erzielen eine Reduzierung der Umpositionierungszeiten um 851 TP3T durch Bohrsequenzen mit nur einer Aufspannung, bei denen alle Bohrungsvorgänge in einer Werkstückaufspannung abgeschlossen werden. Diese Workflow-Konsolidierung behebt direkt die akkumulierten Toleranzprobleme – jede Werkstückumpositionierung birgt das Risiko von Ausrichtungsfehlern, die sich durch aufeinanderfolgende Arbeitsgänge verstärken. Der Wegfall mehrerer Aufspannungen reduziert Handhabungsfehler um 681 TP3T und gewährleistet gleichzeitig konsistente Bezugspunkte während des gesamten Bohrprozesses.
Die hohe Winkelgenauigkeit erweitert das Anwendungsspektrum beim Bohren erheblich. Standardmäßige 5-Achs-Konfigurationen bieten einen Verfahrbereich der B-Achse von -120° bis +30°, gekoppelt mit einer kontinuierlichen 360°-Drehung der C-Achse. Diese Winkelflexibilität ermöglicht Schrägbohren Bearbeitungsvorgänge, bei denen die Mittellinien von Bohrungen die Werkstückoberflächen in nicht senkrechten Winkeln schneiden – eine entscheidende Anforderung für Turbinenkomponenten in der Luft- und Raumfahrt, Drainagesysteme für medizinische Implantate und Anwendungen im Bereich der Präzisionswerkzeuge.
Kernbohranwendungen nutzen diese Möglichkeiten für vielfältige Fertigungsanforderungen. Bohrungen mit komplexem Winkel erfordern eine präzise Winkelpositionierung in Verbindung mit Tiefenkontrolle, insbesondere beim Bohren von Kühlkanälen in Turbinenschaufeln oder Belüftungskanälen in Batteriegehäusen. Tiefbohrarbeiten in superharten Werkstoffen profitieren von der 5-Achsen-Orientierungskontrolle, die Schnittkräfte und Bohrspäneabfuhr über große Bohrtiefen optimiert. Mikrobohranwendungen mit Durchmessertoleranzen innerhalb von 10 Mikrometern nutzen die 5-Achsen-Positionierung, um die Rechtwinkligkeitsvorgaben einzuhalten, die mit herkömmlichen Anlagen nicht zuverlässig erreicht werden können.
Technische Spezifikationen legen die Leistungsgrundlagen für Präzisionsbohrarbeiten fest. 5-Achs-Bearbeitung Die Systeme erreichen eine Positioniergenauigkeit von ±0,005 mm entlang der linearen Achsen, während die Drehachsen eine Positioniergenauigkeit von ±10 Bogensekunden erzielen. Diese Genauigkeitsstandards wirken sich direkt auf die Bohrlochqualität aus: Positionsgenauigkeit, Rechtwinkligkeitstoleranz und Rundheitsspezifikationen verbessern sich, wenn das Bohren in einer stabilen Einzelaufspannung und nicht durch mehrere Aufspannungen erfolgt.
Der Vergleich von 5-Achs-Bohrverfahren und herkömmlichen 3-Achs-Verfahren offenbart grundlegende Unterschiede hinsichtlich Betriebseffizienz, Präzision und Wirtschaftlichkeit. Fertigungsbetriebe, die komplexe Bauteile bearbeiten, stehen vor strategischen Ausrüstungsentscheidungen, bei denen diese Leistungsunterschiede direkten Einfluss auf Produktionsdurchsatz, Qualitätskonstanz und Gesamtfertigungskosten haben.
Bohrvorgänge in einer einzigen Aufspannung bieten durch die Gewährleistung der Werkstückstabilität unmittelbare Vorteile im Arbeitsablauf. Da die Bauteile während des gesamten Bohrvorgangs in gleichbleibender Ausrichtung montiert bleiben, bleibt die Messgenauigkeit ohne Übergänge der Referenzfläche erhalten. Diese geometrische Stabilität reduziert die Werkstückhandhabungsfehler um 681 TP3T im Vergleich zu Mehrspannungssequenzen, bei denen jede Neupositionierung zu potenziellen Fehlausrichtungen führt. Durch den Wegfall von Vorrichtungswechseln entfällt die Rüstzeit vollständig – Vorgänge, die zuvor 2–4 Stunden pro Bauteil in Anspruch nahmen, werden nun in kontinuierlichen Bearbeitungszyklen abgeschlossen.
| Leistungsmetrik | 3-Achs-Bohrung | 5-Achs-Bohrung | Verbesserung |
|---|---|---|---|
| Einrichtungsvoraussetzungen | 3-5 Befestigungselemente pro Komponente | Abschluss einer einzelnen Einrichtung | 85% Zeitreduzierung |
| Genauigkeit von Winkelbohrungen | ±0,015 mm typisch | ±0,003 mm erreichbar | 5-fache Präzisionsverbesserung |
| Fähigkeit zum zusammengesetzten Winkel | Erfordert Sonderanfertigungen | Nativer geometrischer Zugriff | Eliminiert die Einrichtungskosten |
| Zykluszeit (komplexe Teile) | 100%-Baseline | 30-60% der Basiszeit | 40-70% höherer Durchsatz |
| Akkumulierter Toleranzfehler | Verbindungen mit jeder Konfiguration | Bezugssystem mit einem einzigen Bezugspunkt | 68% Fehlerreduzierung |
Die deutlichsten Präzisionsverbesserungen zeigen sich beim Bohren mit komplexen Winkeln. Herkömmliche 3-Achs-Maschinen benötigen aufwendige Spannsysteme, um die Werkstückoberflächen senkrecht zum Bohrwinkel auszurichten – jede Spannvorrichtung verursacht Positionierungsfehler, die sich in der Toleranzkette summieren. 5-Achs-Systeme richten die Bohrspindel direkt auf den erforderlichen Anstellwinkel aus und halten dabei die Werkstückposition konstant. Dadurch wird eine Genauigkeit beim Bohren mit komplexen Winkeln von ±0,003 mm erreicht, im Vergleich zu den bei herkömmlichen Mehrspannvorrichtungen üblichen Toleranzen von ±0,015 mm.
Die Zykluszeitreduzierungen skalieren proportional mit der Komplexität des Bohrvorgangs. Bauteile mit mehreren Lochmustern in unterschiedlichen Winkeln weisen auf 5-Achs-Plattformen einen höheren Durchsatz mit der 40-70% auf. Der Leistungsunterschied nimmt mit der Bauteilkomplexität zu: Einfache Muster mit 4–6 Löchern zeigen moderate Zeitverbesserungen, während Luft- und Raumfahrtbauteile mit über 50 Kühlbohrungen in verschiedenen Winkeln durch kontinuierliche Bohrsequenzen, die auf 3-Achs-Maschinen nicht möglich sind, nahezu maximale Zykluszeitvorteile erzielen.
Sich kreuzende Lochmuster veranschaulichen geometrische Fähigkeiten, die einzigartig sind für Fünf-Achs-Bearbeitung Systeme. Wenn Bohrvorgänge präzise Bohrlochwinkel erfordern – wie sie beispielsweise bei Fluidverteilern, Kühlkanälen und Hydraulikkomponenten üblich sind – gewährleistet die 5-Achsen-Positionierung Ausrichtungstoleranzen entlang der Mittellinie, die mit herkömmlichen Vorrichtungen nicht zuverlässig erreicht werden können. Die Rotationsachsensteuerung hält den Bohrwinkel über die gesamte Bohrtiefe konstant und verhindert so die Bohrlochverlaufsabweichung, die bei der Verwendung von Winkelvorrichtungen an konventionellen Geräten auftritt.
Materialabtragsstrategien profitieren von einer optimierten Schnittkraftausrichtung. Fünf-Achs-Bohrverfahren positionieren die Werkzeuge in idealen Eingriffswinkeln, wodurch die seitlichen Schnittkräfte minimiert, die Werkzeugdurchbiegung reduziert und die Werkzeugstandzeit um 25–401 TP3T verlängert wird. Diese Kraftoptimierung erweist sich als besonders wertvoll beim Bohren von schwer zu bearbeitenden Werkstoffen wie Titanlegierungen, Inconel-Superlegierungen und Keramikverbundwerkstoffen, da die Schnittkräfte hier die Bohrlochqualität und den Werkzeugverschleiß maßgeblich beeinflussen.
Fortschrittliche 5-Achs-Bohrtechnologien bewältigen branchenspezifische Fertigungsherausforderungen in Sektoren, in denen präzise Bohrungen direkten Einfluss auf die Bauteilleistung, die Einhaltung gesetzlicher Vorschriften und die Wirtschaftlichkeit der Produktion haben. Die folgende Anwendungsanalyse untersucht kritische Bohranforderungen und technische Lösungen in der Luft- und Raumfahrt, der Medizintechnik, der Automobilindustrie, der Ölförderung und der Werkzeugherstellung.
Komponenten von Turbinentriebwerken stellen die anspruchsvollsten Bohranwendungen in der Luft- und Raumfahrtindustrie dar. Moderne Turbinenschaufeln weisen komplexe Kühlbohrungsmuster auf – oft 50 bis 200 Bohrungen pro Schaufel –, die Durchmesser von 0,1 mm bis 3 mm erfordern und in Winkeln von 15° bis 45° zur Schaufeloberfläche gebohrt werden müssen. Diese Kühlkanäle halten die Betriebstemperaturen innerhalb der metallurgischen Grenzen, wodurch die Genauigkeit der Bohrungsposition und des Bohrwinkels zu entscheidenden Leistungsparametern werden.
Fünf-Achs-Bohrsysteme führen diese Bearbeitungsvorgänge durch koordinierte Bewegungen aus, die optimale Anstellwinkel gewährleisten und gleichzeitig die Krümmung der Schaufelprofile ausgleichen. Eine Positioniergenauigkeit von ±0,005 mm stellt sicher, dass die Kühlbohrungen mit den Geometrien der internen Kanäle übereinstimmen, während die Winkelkontrolle Abweichungen der Durchbruchpositionen von mehr als ±0,5° verhindert. Hersteller, die Titan und Nickelbasis-Superlegierungen verarbeiten, erreichen Zykluszeiten von 60%, die deutlich kürzer sind als bei EDM-Verfahren, und halten dabei die Qualitätsstandards für Bohrungen ein, die sowohl den OEM-Spezifikationen als auch den behördlichen Anforderungen an die Lufttüchtigkeit entsprechen.
Die Bearbeitung von Schaufelprofilen stellt aufgrund des Verhältnisses von Tiefe zu Durchmesser von über 10:1 bei beengten Schaufelgeometrien eine zusätzliche Herausforderung dar. Fortschrittliche Bohrstrategien umfassen Tiefbohrzyklen, Hochdruckkühlung und Echtzeit-Werkzeugverschleißüberwachung, um die Bohrlochgeradheitstoleranzen von 0,1 mm über eine Bohrtiefe von 30 mm einzuhalten. Die 5-Achs-Plattform ermöglicht optimale Späneabfuhrwege und verhindert so Späneansammlungen – ein entscheidender Faktor beim Bohren der in modernen Turbinentriebwerken verwendeten hochfesten Legierungen.
Die Herstellung orthopädischer Implantate erfordert biokompatible Bohrverfahren, die die Oberflächenintegrität erhalten und gleichzeitig komplexe Drainagekanalgeometrien ermöglichen. Hüft- und Knieimplantate verfügen über Fenestrierungsmuster, die die Osseointegration durch Knocheneinwachswege fördern. Diese Drainagekanäle erfordern präzise Positionierungstoleranzen von ±0,05 mm, um die Lastverteilungseigenschaften zu gewährleisten, die während der Gerätevalidierung mittels Finite-Elemente-Analyse verifiziert wurden.
Fünfachsige Bohrplattformen bearbeiten Titanlegierungen in medizinischer Qualität (Ti-6Al-4V) und Kobalt-Chrom-Werkstoffe und halten dabei Oberflächengütevorgaben unter Ra 0,8 μm ein – unerlässlich für Biokompatibilität und Dauerfestigkeit. Mehrachsenpositionierung Dadurch werden Spannungskonzentrationen beseitigt, die bei Bohrarbeiten durch die Erzeugung von Oberflächenunregelmäßigkeiten entstehen, wodurch die zur Erreichung der von der FDA vorgeschriebenen Oberflächenqualitätsstandards erforderlichen Nachbearbeitungsschritte reduziert werden.
Die Herstellung chirurgischer Instrumente erweitert diese Präzisionsanforderungen auf Bohrungen mit kleineren Durchmessern. Endoskopische Werkzeuge, arthroskopische Shaver und mikrochirurgische Instrumente benötigen Arbeitskanäle mit Durchmessern von 0,5 mm bis 5 mm, die durch komplexe, gekrümmte Oberflächen gebohrt werden müssen. Die geometrische Freiheit von 5-Achs-Systemen ermöglicht Bohrwinkel, die eine optimale Schnittgeometrie über die gesamte Werkzeuglänge gewährleisten und so die Verschlechterung der Bohrgenauigkeit verhindern, die bei herkömmlichen Geräten beim schrägen Bohren durch verlängerte Werkzeugvorsprünge auftritt.
Die Batterieträger in Elektrofahrzeugplattformen verfügen über umfangreiche Belüftungsbohrungen zur Temperaturregulierung der Lithium-Ionen-Zellen. Diese Kühlsysteme benötigen 200 bis 500 Präzisionsbohrungen pro Träger, die in spezifischen Winkeln gebohrt werden, um die Luftstromverteilung zu optimieren und gleichzeitig die strukturelle Integrität der dünnwandigen Aluminiumprofile zu gewährleisten. Eine Positionsgenauigkeit von ±0,1 mm sichert die korrekte Ausrichtung der Belüftungsöffnungen auf die Wärmemanagementkanäle, während die Spezifikationen für die Lochkantenqualität die Entstehung von Rissen in zyklisch belasteten Strukturen verhindern.
Die Komponenten von Elektromotorgehäusen stellen ähnliche Anforderungen an die Bohrungen, da die Integration von Kühlkanälen die Leistungsdichte und die thermische Leistung beeinflusst. Präzisionsbohrungen mit Durchmessern von 3 mm bis 12 mm müssen mit den Schnittstellen externer Wärmetauscher ausgerichtet sein, ohne dabei elektromagnetische Wicklungen und Lagerstrukturen zu beeinträchtigen. Fünfachsige Bohrbearbeitungen ermöglichen die Fertigung dieser Bohrungen in einer einzigen Aufspannung und gewährleisten so Positionsgenauigkeit, die mit herkömmlichen Maschinen durch mehrstufige Bearbeitungssequenzen nicht erreichbar wäre.
Die Herstellung von PDC-Bohrmeißeln (Polycrystalline Diamond Compact) zählt zu den technisch anspruchsvollsten Bohrprozessen in der Erdölförderanlagenproduktion. Diese Schneidstrukturen bestehen aus präzisionsgeschliffenen PDC-Schneidwerkzeugen, die in spezifischen Winkeln und Positionen auf den Meißelkörpern montiert sind und extremen Bedingungen im Bohrloch standhalten müssen. Die Positionierungsgenauigkeit der Montagebohrungen muss innerhalb von ±0,025 mm liegen, um die Vorgaben für die Schneidwerkzeugausrichtung einzuhalten. Die Bohrlochqualität beeinflusst direkt die strukturelle Integrität unter den zyklischen Belastungen während des Bohrvorgangs.
Komplexe Ölbohrkronengeometrien erfordern Toleranzen im Sub-10-Mikron-Bereich bei den Lochmustern, die Flüssigkeitszirkulationsdüsen, Montagepunkte für Messplatten und Hartmetalleinsätze aufnehmen müssen. Fünfachsige Laserbohrsysteme Diese Merkmale werden durch Hybridverfahren bearbeitet, die mechanisches Vorbohren mit Laserbearbeitung kombinieren, um Oberflächengüten unter Ra 0,4 μm zu erreichen. Die präzise Positionierung gewährleistet Düsenausrichtungstoleranzen, die die hydraulische Leistung über die gesamte Lebensdauer des Bohrers optimieren.
Die Herstellung von Hartmetall-Schaftfräsern erfordert präzises Bohren von Kühlmittelkanälen, die sich durch den Werkzeugkörper bis zu den Schneidkanten erstrecken. Diese internen Kanäle – typischerweise mit einem Durchmesser von 0,5 mm bis 2 mm – müssen über Längen von mehr als 50 mm eine Geradheitstoleranz von 0,05 mm aufweisen, um einen gleichmäßigen Kühlmittelfluss bei Hochgeschwindigkeitsbearbeitungen zu gewährleisten. Fünf-Achs-Bohrplattformen richten das Werkzeug so aus, dass die Eintrittspunkte der Bohrung optimiert und gleichzeitig Ablenkkräfte kompensiert werden, die die Geradheit der Bohrung bei herkömmlichen Anlagen beeinträchtigen würden.
Die Fertigung von PCD-Schneidwerkzeugen (polykristalliner Diamant) erweitert die Präzisionsanforderungen durch Bohrbearbeitungen an superharten Materialien. Spanabfuhrkanäle in PCD-Wendeschneidplatten erfordern lasergestützte Bohrtechniken, die ein Verhältnis von Schnitttiefe zu Schnittbreite von 100:1 erreichen und gleichzeitig die Spezifikationen für die Schneidenqualität einhalten, um die Schneidleistung zu erhalten. Die Integration von Femtosekundenlasersysteme Die 5-Achsen-Positionierungssteuerung ermöglicht Bearbeitungsstrategien, die mit herkömmlichen mechanischen Bohrverfahren nicht möglich sind, und erzielt Lochgeometrien, die die Spanflusseigenschaften in anspruchsvollen Bearbeitungsanwendungen optimieren.
Moderne 5-Achs-Bohrplattformen integrieren fortschrittliche Prozesstechnologien, die die Einsatzmöglichkeiten über das konventionelle mechanische Bohren hinaus erweitern. Diese technologischen Verbesserungen adressieren spezifische Herausforderungen in der Fertigung, darunter die Bearbeitung von extrem harten Materialien, die Anforderungen an die Präzision beim Tiefbohren und Qualitätsvalidierungsprotokolle, die eine gleichbleibende Leistung über alle Produktionsvolumina hinweg gewährleisten.
Femtosekundenlasersysteme, integriert in 5-Achs-Bearbeitungszentren, revolutionieren das Bohren in Werkstoffen, die herkömmlichen Bearbeitungsmethoden widerstehen. Diese ultraschnellen Laserplattformen liefern Pulsdauern im Bereich von Quadrillionstel Sekunden (10⁻¹⁵ Sekunden) und tragen Material durch Kaltablation ab, wodurch Wärmeeinflusszonen und mechanische Spannungskonzentrationen vermieden werden. Das Ergebnis: Bohrvorgänge in PCD, PCBN, CVD-Diamant und Keramikverbundwerkstoffen mit einem Tiefen-Breiten-Verhältnis von 100:1 und einer Positioniergenauigkeit von ±3 μm.
Die technischen Vorteile zeigen sich in der präzisen Energiezufuhr, die Material auf atomarer Ebene verdampft, ohne das umgebende Substrat thermisch zu schädigen. Beim Bohren von Kühllöchern in keramischen Turbinenkomponenten oder beim Erstellen von Evakuierungskanälen in Diamantschneidplatten erhält die Femtosekundenlaserbearbeitung die Materialeigenschaften über den gesamten Lochumfang hinweg – Mikrorisse und die Bildung von Umwandlungsschichten werden vermieden, die bei herkömmlichen Bohr- oder EDM-Verfahren auftreten.
Die Integrationsarchitektur kombiniert Laserstrahlführungssysteme mit einer 5-Achsen-Bewegungssteuerung mittels synchronisierter Positionierprotokolle. Der Laserfokuspunkt behält während der gesamten Achsenbewegung seine präzise Position zur Werkstückoberfläche bei und kompensiert so Oberflächenkonturabweichungen unter Beibehaltung der Fokusgeometrie. Diese Koordination ermöglicht Bohrvorgänge entlang komplexer dreidimensionaler Bahnen und erzeugt Lochgeometrien, die mit herkömmlichen Verfahren mit festem Winkel nicht realisierbar sind.
Die Steuerung des Rotationswerkzeugmittelpunkts (RTCP) ist eine entscheidende Funktion für die Aufrechterhaltung der Bohrgenauigkeit bei gleichzeitiger Mehrachsenbewegung. Dieser fortschrittliche kinematische Algorithmus berechnet eine Positionskompensation in Echtzeit, die die Werkzeugspitze bzw. den Laserfokuspunkt relativ zur Werkstückoberfläche stationär hält, selbst wenn sich die Werkstückausrichtung während des Bohrvorgangs durch die Rotationsachsen ändert.
Die technische Umsetzung überwacht die momentanen Positionen entlang aller fünf Achsen und berechnet geometrische Beziehungen, die die Koordinaten des Werkzeugmittelpunkts trotz Rotation um die B- und C-Achse beibehalten. Beim Bohren von Bohrungen mit komplexem Winkel, bei denen sich die Werkstückausrichtung während des Vorgangs ändert, gewährleistet die RTCP-Funktionalität die Genauigkeit der Bohrungsposition, die sich andernfalls durch unkompensierte Achsenbewegungen verschlechtern würde. Fertigungsprozesse erreichen eine Winkelpositionierung der Bohrung innerhalb von ±10 Bogensekunden – entscheidend für die Kühlbohrungsmuster von Turbinenschaufeln, da die Ausrichtung der Bohrungsmittellinie die aerodynamische Leistung direkt beeinflusst.
Praktische Bohranwendungen demonstrieren die Vorteile der RTCP-Technologie bei der Bearbeitung gekrümmter Oberflächen oder komplexer Geometrien, die kontinuierliche Änderungen der Bohrerausrichtung erfordern. Kugelförmige Bauteile, toroidale Formen und Freiformflächen profitieren von der adaptiven Werkzeugpositionierung, die eine optimale Schnittgeometrie während des gesamten Bohrvorgangs gewährleistet. Das Ergebnis: Gleichbleibende Bohrungsqualität über die gesamte Bauteiloberfläche anstatt Genauigkeitseinbußen in Bereichen, in denen herkömmliche Geräte die Anstellwinkel des Bohrers beeinträchtigen.
Die wassergeführte Lasertechnologie eröffnet revolutionäre Möglichkeiten für Tiefloch-Mikrobohrungen. Dieses fortschrittliche Verfahren kombiniert Laserenergie mit Hochdruckwasserstrahlen, die gleichzeitig Bohrspäne entfernen, Restwärme abführen und den Laserstrahl durch größere Bohrtiefen führen. wassergeführtes Lasersystem Erreicht eine außergewöhnliche Präzision bei superharten Materialien und liefert Tiefen-Breiten-Verhältnisse von 100:1 mit einer Positionsgenauigkeit von ±3μm während des gesamten Bohrvorgangs.
Der technische Mechanismus lenkt Laserpulse durch einen laminaren Wasserstrahl, der die Strahlkohärenz aufrechterhält und gleichzeitig einen kontinuierlichen Abtransport des Bohrguts gewährleistet. Zwischen den Laserpulsen entfernt der Wasserstrahl abgetragene Materialpartikel und führt thermische Energie ab – entscheidende Faktoren beim Bohren von Materialien mit geringer Wärmeleitfähigkeit wie Keramik und Diamantverbundwerkstoffen. Die Ingenieurteams beobachten erweiterte Prozessfenster für tiefe Mikrobohrungen, wobei die Bohreigenschaften über Bohrtiefen hinweg stabil bleiben, bei denen herkömmliche mechanische Bohrverfahren durch Spanablagerungen oder Werkzeugdurchbiegung versagen würden.
Die praktische Umsetzung kombiniert Wasserzufuhrsysteme mit präziser Bewegungssteuerung und synchronisiert die Laserpulszeiten mit der Achsenpositionsrückmeldung. Bohrprozesse gewährleisten eine gleichbleibende Materialabtragsrate über große Bohrtiefen und vermeiden die für konventionelle Tiefbohrverfahren typische Kegelbildung und Lochdurchmesserabweichung. Die Anwendungsbereiche reichen von Kraftstoffeinspritzdüsen mit 0,1 mm großen Bohrungen in 10 mm Tiefe bis hin zu Kühlkanälen in Keramikbauteilen, bei denen thermische Schäden unterhalb messbarer Schwellenwerte bleiben müssen.
Echtzeit-Schwingungskompensationssysteme überwachen die Maschinendynamik während des Bohrvorgangs und implementieren korrigierende Bewegungssteuerung, um Werkzeugdurchbiegungen zu reduzieren. Hochfrequente Beschleunigungssensoren, die an verschiedenen Maschinenkomponenten angebracht sind, erfassen Schwingungsmuster, die auf drohendes Rattern oder zu hohe Schnittkräfte hinweisen. Fortschrittliche Regelalgorithmen verarbeiten diese Sensordaten und passen Vorschubgeschwindigkeit und Spindeldrehzahl innerhalb von Millisekunden an, um stabile Bohrbedingungen zu gewährleisten.
Die technische Umsetzung nutzt Vorhersagemodelle, die Schwingungsmuster mit der Bohrungsqualität korrelieren. Sobald Sensordaten auf eine beginnende Instabilität hinweisen, passt das Steuerungssystem die Prozessparameter an – beispielsweise durch Reduzierung der Vorschubgeschwindigkeit um 5–151 µm oder Anpassung der Spindeldrehzahl um 100–300 U/min –, um optimale Schnittbedingungen wiederherzustellen. Durch diese adaptiven Strategien wird in der Fertigung eine Verbesserung der Bohrungsrundheit um 351 µm erzielt. Die Rundheitsabweichungen bleiben dabei konstant unter 0,003 mm, selbst beim Bohren schwieriger Werkstoffe oder der Bearbeitung dünnwandiger, verformungsanfälliger Strukturen.
Die Werkzeugdurchbiegungsüberwachung erweitert diese Möglichkeiten durch kontinuierliche Positionsverifizierung. Der Vergleich der Sollpositionen der Werkzeuge mit den tatsächlichen, von maschinenmontierten Sensoren erfassten Koordinaten zeigt die Durchbiegungsgrößen, die die Genauigkeit der Bohrungspositionierung beeinflussen. Kompensationsalgorithmen passen die programmierten Werkzeugwege in Echtzeit an und implementieren Offsetwerte, die die Schneidkanten so positionieren, dass die Zielbohrungskoordinaten trotz der auf die Werkzeugüberstände wirkenden Durchbiegungskräfte erreicht werden.
Automatisierte Messtaster-Verifizierungssysteme, die in 5-Achs-Bohrzentren integriert sind, ermöglichen die kontinuierliche Qualitätsprüfung, ohne dass die Bauteile aus den Vorrichtungen entnommen werden müssen. Messtaster oder Laserscanner erfassen die Bohrlochpositionen unmittelbar nach Abschluss des Bohrvorgangs und vergleichen die gemessenen Koordinaten mit den CAD-Vorgaben, um die Positionsgenauigkeit innerhalb von 5 Mikrometern zu überprüfen.
Das Qualitätssicherungsprotokoll etabliert einen geschlossenen Regelkreis, in dem Messdaten die nachfolgenden Arbeitsschritte steuern. Sobald die Tastprüfung Positionsabweichungen nahe den Toleranzgrenzen feststellt, korrigiert das Steuerungssystem die verbleibenden Lochmuster im selben Werkstück. Dieser adaptive Ansatz verhindert die Fortpflanzung kumulativer Fehler in den Bohrsequenzen und gewährleistet konsistente Positionsbeziehungen zwischen den Löchern bei Bauteilen mit Hunderten von Präzisionsmerkmalen.
Die Integration der statistischen Prozesskontrolle erfasst Messdaten über Produktionschargen hinweg, überwacht die Genauigkeit der Bohrungspositionen und identifiziert systematische Abweichungen, bevor fehlerhafte Bauteile die Endprüfung erreichen. Fertigungsingenieure greifen auf Echtzeit-Qualitäts-Dashboards zu, die Kennwerte (Cpk-Werte) anzeigen und die Produktionsteams alarmieren, wenn Prozessabweichungen sich den Spezifikationsgrenzen annähern. Dieses proaktive Qualitätsmanagement reduziert die Ausschussrate um 40–60¹³T im Vergleich zu nachgelagerten Prüfverfahren, bei denen fehlerhafte Merkmale teure Nacharbeiten oder die Ausschussquote der Bauteile erfordern.
Das umfassende Portfolio an 5-Achs-Bohrplattformen von OPMT Laser deckt vielfältige Fertigungsanforderungen ab. Die anwendungsoptimierten Konfigurationen bieten ein ausgewogenes Verhältnis zwischen Präzision, Produktionsdurchsatz und Gesamtbetriebskosten. Die folgenden Systemspezifikationen beschreiben die technischen Möglichkeiten vertikaler Bearbeitungszentren, hybrider lasermechanischer Plattformen und revolutionärer wassergeführter Laserbohrsysteme für die Bearbeitung extrem harter Materialien.
Der Licht 5X 40V Die Präzisionsbohrplattform von OPMT ist für die Herstellung von Schneidwerkzeugen und die Bearbeitung hochpräziser Kleinteile optimiert. Das System bietet einen Arbeitsbereich von 400 mm × 250 mm × 300 mm mit HSK-A63-Spindelanschluss und gewährleistet die für Mikrobohrarbeiten in PKD-, PCBN- und CVD-Diamantwerkzeugen erforderliche Steifigkeit und Präzision.
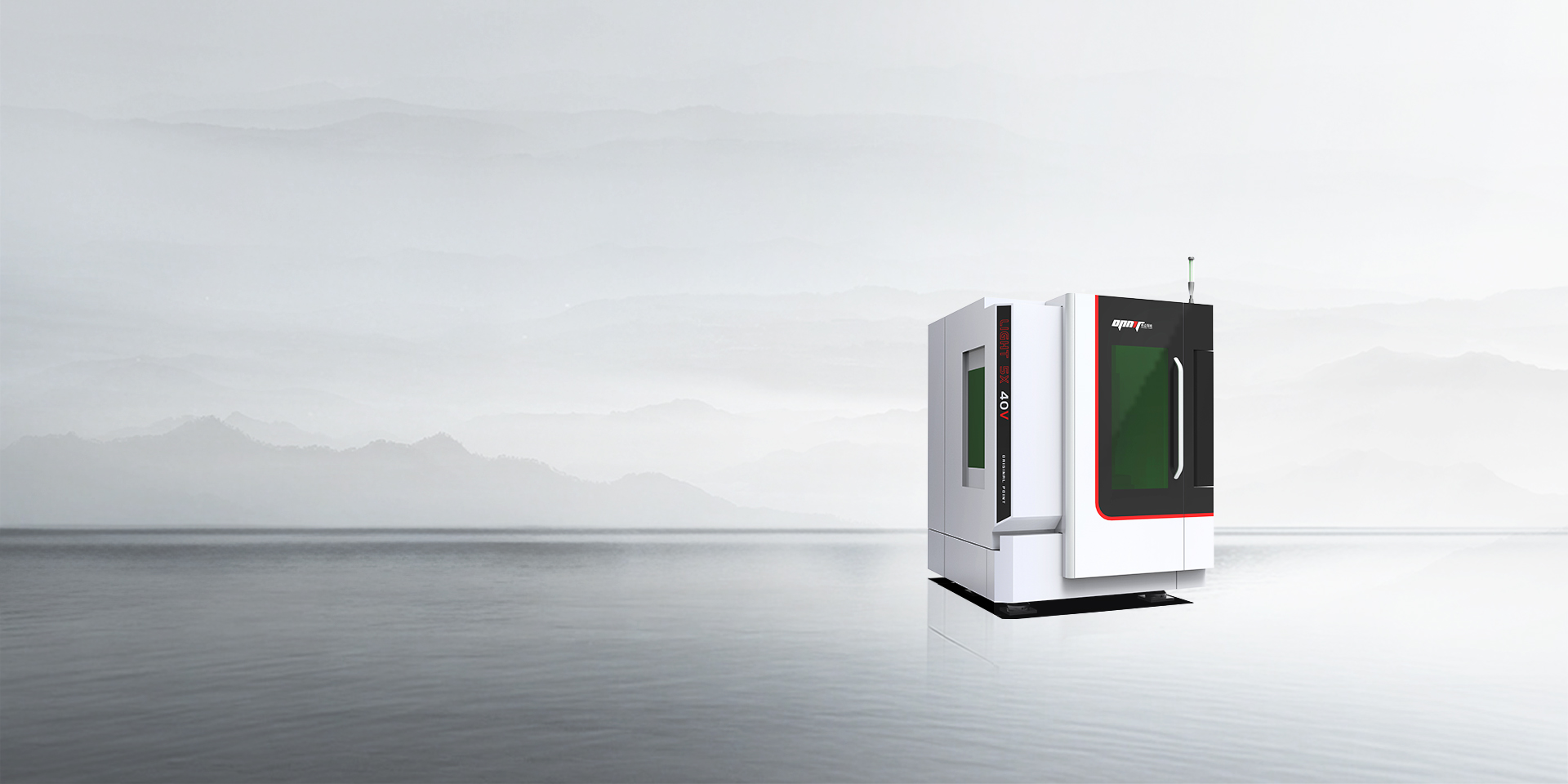

Die technischen Spezifikationen setzen Leistungsstandards für Präzisionsbohrungen. Die Positioniergenauigkeit der Linearachse erreicht eine Wiederholgenauigkeit von ±0,005 mm in X-, Y- und Z-Richtung. Die Rotation der B-Achse (-120° bis 0°) und die kontinuierliche Rotation der C-Achse (360°) ermöglichen den vollen Winkelbereich für Bohrungen mit komplexen Winkeln. Eilganggeschwindigkeiten von bis zu 30 m/min minimieren die Leerlaufzeiten, während Vorschubgeschwindigkeiten von bis zu 20 m/min den Materialabtrag in anspruchsvollen Anwendungen optimieren.
Das integrierte Femtosekundenlasersystem ermöglicht Bohrarbeiten in superharten Werkstoffen mit Bearbeitungsgenauigkeiten im Bereich von 0,003 mm. Laserpulse im Nanosekundenbereich sorgen für eine präzise Energiezufuhr, die Material durch Kaltablation abträgt und so Wärmeeinflusszonen vermeidet, welche die mechanischen Eigenschaften beeinträchtigen. Anwendungsbereiche sind unter anderem die Fertigung von Präzisionswerkzeugen, beispielsweise für Kühlbohrungen in Schaftfräsern, Spanbrecher für PKD-Wendeschneidplatten und Kühlkanäle für Keramikbauteile.
Die Werkstückhandhabung ermöglicht die Bearbeitung von Bauteilen bis zu 10 kg auf dem C-Achsen-Drehtisch. Für Spezialanwendungen können Werkzeugdurchmesser bis zu 200 mm verwendet werden. Die HSK-A63-Schnittstelle gewährleistet die für die Bohrungsqualität bei Hochgeschwindigkeitsbohrvorgängen unerlässliche Werkzeugaufnahmestabilität. Die direkt angetriebenen Motoren der B- und C-Achse eliminieren Spiel, das andernfalls die Winkelpositioniergenauigkeit beeinträchtigen würde.
Die Plattform 563V erweitert die Bohrkapazitäten auf die Anforderungen der Großkomponentenfertigung und bietet Achsverfahrwege von 700 mm × 780 mm × 550 mm bei einer Tischkapazität von 800 kg. Diese Konfiguration eignet sich für das Bohren von Strukturbauteilen in der Luft- und Raumfahrt, die Bearbeitung von Batterieträgern für die Automobilindustrie sowie die Herstellung von Ölbohranlagen, wo die Bauteilgrößen die Kapazitäten kleiner Bearbeitungszentren übersteigen.
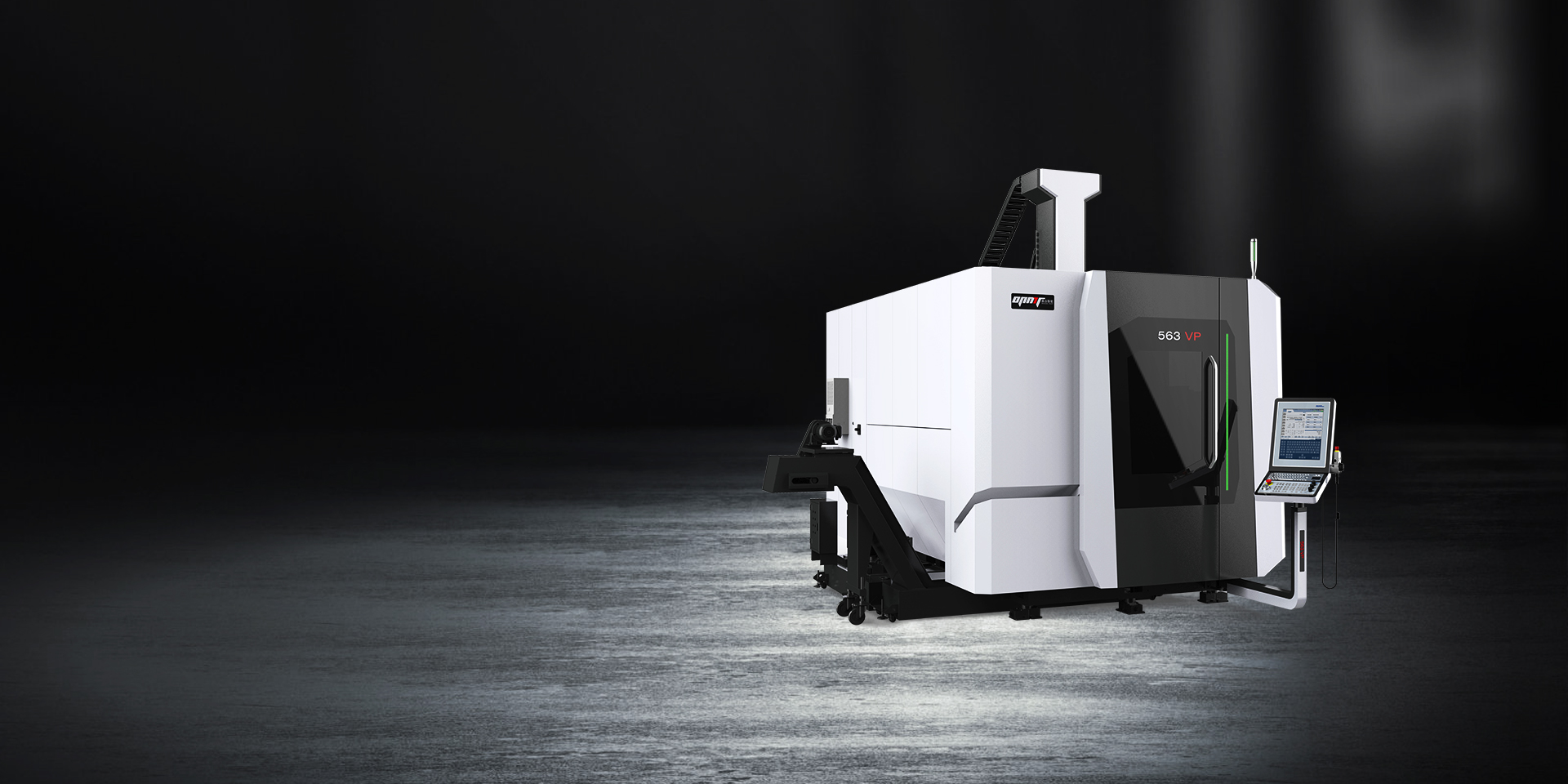

Die Direktantriebsarchitektur der Wechselstromachsen unterscheidet die 563V von Konkurrenzprodukten. Beide Drehachsen nutzen Drehmomentmotoren, wodurch mechanische Übertragungskomponenten entfallen – Getriebe, Riemen oder Kupplungen verursachen weder Spiel noch Nachgiebigkeit im Drehpositioniersystem. Das Ergebnis: eine Positioniergenauigkeit von ±10 Bogensekunden mit einer Wiederholgenauigkeit von ±5 Bogensekunden über den gesamten B-Achsen-Bereich (-120° bis +30°) und kontinuierliche Rotation der C-Achse.
Die Spezifikationen der Linearachse entsprechen den Leistungsstandards des gesamten Portfolios vertikaler Bearbeitungszentren von OPMT. Eine Positioniergenauigkeit von ±0,005 mm wird mit einer Wiederholgenauigkeit von ±0,003 mm kombiniert, während Eilganggeschwindigkeiten von bis zu 48 m/min die Zykluszeiten für Bauteile mit umfangreichen Lochmustern über große Arbeitsbereiche verkürzen. Die Portalbauweise mit beweglichem Träger gewährleistet die Steifigkeit über den gesamten Verfahrweg der Y-Achse und verhindert so die Trägerdurchbiegung, die die Positioniergenauigkeit von Bohrungen bei Kragarm-Maschinen beeinträchtigt.
Die Flexibilität beim Bohren wird durch das 30-fach Werkzeugmagazin gewährleistet, das Schneidwerkzeuge mit einem Einzelgewicht von bis zu 6 kg und einer maximalen Länge von 300 mm aufnimmt. Der automatische Werkzeugwechsel erfolgt in weniger als 8 Sekunden und minimiert so die Stillstandszeiten, die bei Bauteilen mit unterschiedlichen Bohrergrößen anfallen. Die schirmförmige Magazinkonstruktion schützt die Werkzeuge vor Kühlmittelverunreinigungen und ermöglicht gleichzeitig einen schnellen Werkzeugzugriff während des gesamten Bohrvorgangs.
Der WJC532V revolutioniert das Bohren von superharten Materialien durch wassergeführte Lasertechnologie. Diese fortschrittliche Plattform kombiniert Laserenergiezufuhr mit Hochdruckwasserstrahlen, die gleichzeitig Bohrspäne entfernen, thermische Energie abführen und den Laserstrahl durch große Bohrtiefen führen. Das Ergebnis: Bohrvorgänge mit einem Tiefen-Breiten-Verhältnis von 100:1 und einer Positioniergenauigkeit von ±3 μm bei Materialien wie Keramikverbundwerkstoffen, PCD und CVD-Diamant.
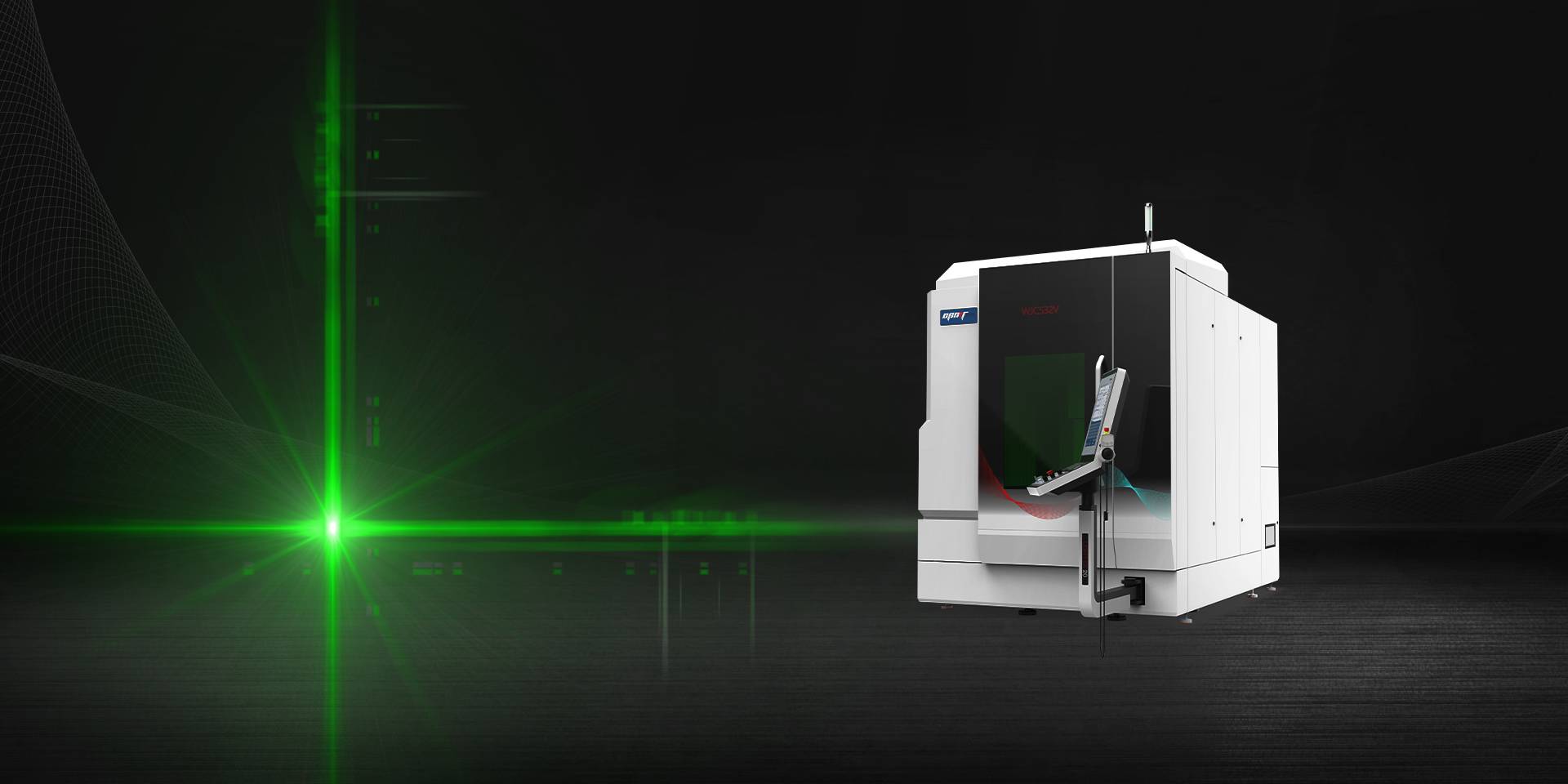
Die Wasserstrahl-Fasertechnologie ist die Kerninnovation, die dieses System von herkömmlichen Laserbohrplattformen unterscheidet. Hochdruckwasserstrahlen – präzise geformt durch spezielle Düsengeometrien – gewährleisten eine laminare Strömung und erhalten so die Kohärenz des Laserstrahls während des gesamten Bohrvorgangs. Das Wasser erfüllt dabei mehrere Prozessfunktionen: Es kühlt die Ablationszone, um thermische Schäden zu vermeiden, spült Bohrspäne von der Bohrstelle und führt nachfolgende Laserimpulse entlang des vorgegebenen Bohrlochverlaufs.
Die Leistungsspezifikationen demonstrieren Möglichkeiten, die mit mechanischen Bohrverfahren nicht realisierbar sind. Bohrarbeiten in Keramik-Turbinenbauteilen erreichen eine Bohrungsgeradheit von unter 0,1 mm über eine Tiefe von 30 mm – eine Präzision, die mit herkömmlichen Bohrverfahren bei spröden, unter mechanischer Belastung bruchgefährdeten Materialien nicht zuverlässig erzielt werden kann. Oberflächengütevorgaben unter Ra 0,4 μm machen Nachbearbeitungen überflüssig, und der Verzicht auf mechanische Werkzeugkräfte ermöglicht das Bohren in dünnwandigen Strukturen, die sich unter herkömmlichen Schnittbelastungen verformen oder brechen würden.
Die Anwendungsbereiche reichen von Wärmedämmschichten für die Luft- und Raumfahrt über medizinische Keramikimplantate und die Bearbeitung von Halbleiterwafern bis hin zur Herstellung von Präzisionsschneidwerkzeugen. Die Vielseitigkeit erstreckt sich auf verschiedene Materialarten – Aluminiumoxidkeramik, Zirkonoxid-Biokeramik, Siliziumkarbid-Verbundwerkstoffe und polykristalline Diamantwerkzeuge lassen sich alle erfolgreich auf derselben Maschinenplattform verarbeiten, indem Parameter optimiert werden, anstatt spezielle Werkzeuganforderungen zu erfüllen.
Die Hybridbohrstrategie von OPMT kombiniert mechanisches Vorbohren mit Laserbearbeitung, um sowohl Produktivität als auch Oberflächenqualität zu optimieren. Dieser integrierte Ansatz nutzt die hohe Abtragsleistung des Hartmetallbohrens zur Erzeugung großer Bohrungen, gefolgt von der Laserbearbeitung, die eine Maßgenauigkeit und Oberflächengüte erreicht, die mit rein mechanischen Methoden nicht zu erzielen ist.
Der technische Arbeitsablauf umfasst das mechanische Bohren auf die endgültigen Lochabmessungen von 90–951 TP3T, wodurch die grundlegende Lochgeometrie erstellt und der Großteil des Materials mit hohen Vorschubgeschwindigkeiten abgetragen wird. Die anschließende Laserbearbeitung entfernt den verbleibenden Materialüberschuss – typischerweise 0,05 mm bis 0,15 mm radial – durch kontrollierte Ablation und erzielt so eine Oberflächenrauheit unter Ra 0,2 μm. Dieses zweistufige Verfahren kombiniert die Produktivität des mechanischen Bohrens (gemessen in mm³/min) mit der Präzision des Lasers (gemessen in Mikrometern) und bietet so die Wirtschaftlichkeit des konventionellen Bohrens mit der Qualität moderner Laserbearbeitung.
Anwendungen erweisen sich insbesondere beim Bohren von schwer zu bearbeitenden Werkstoffen wie Titanlegierungen, Inconel-Superlegierungen und Keramikmatrix-Verbundwerkstoffen als vorteilhaft. Mechanisches Vorbohren entfernt effizient Materialmengen, selbst unter schwierigen Schnittbedingungen. Die Laserbearbeitung beseitigt Gratbildung, Umwandlungsschichten und Oberflächenunebenheiten, die die Bohrlochqualität beim mechanischen Vollbohren beeinträchtigen. Diese Hybridstrategie reduziert die Gesamtbearbeitungszeit im Vergleich zu rein laserbasierten Verfahren um 30–40 Minuten und gewährleistet gleichzeitig die für Anwendungen in der Luft- und Raumfahrt sowie der Medizintechnik erforderlichen Präzisionsvorgaben.
Die Ingenieurteams von OPMT passen Standardplattformen an die spezifischen Anforderungen verschiedener Zielbranchen an. Hersteller von Ölbohranlagen erhalten Systemkonfigurationen mit speziellen Vorrichtungen für PDC-Bohrmeißel, automatisierten Ladesystemen für die Serienfertigung und Prüfprotokollen zur Überprüfung der Bohrlochpositionen gemäß API-Spezifikationen. Anwendungen in der Luft- und Raumfahrt integrieren Koordinatenmessprotokolle, Chargenrückverfolgbarkeitssysteme und Dokumentationspakete, die die Qualitätsmanagementanforderungen der AS9100 erfüllen.
Bei der Konfiguration von Medizinprodukten liegt der Schwerpunkt auf biokompatiblen Verarbeitungsprotokollen, einschließlich reinraumkompatibler Gehäuse, validierter Reinigungsverfahren und Materialrückverfolgbarkeitssysteme, die für die Registrierung von Medizinprodukten bei der FDA erforderlich sind. Automobilproduktionssysteme Integration von Automatisierungslösungen für hohe Produktionsvolumina, einschließlich robotergestützter Beladung, bildgestützter Positionierung und statistischer Prozesskontrolle, um die Leistungsfähigkeit über Produktionsläufe mit Millionen von Komponenten hinweg aufrechtzuerhalten.
Quantifizierbare Leistungsspezifikationen bilden die technische Grundlage für die Bewertung von 5-Achs-Bohrsystemen im Hinblick auf Fertigungsanforderungen. Die folgenden Kennzahlen definieren Positioniergenauigkeit, Geschwindigkeit, Materialverträglichkeit, Bohrlochqualität und Produktionseffizienzsteigerungen, die Investitionsentscheidungen für Präzisionsbohrarbeiten rechtfertigen.
Die Positioniergenauigkeit der Linearachsen in X-, Y- und Z-Richtung ist die grundlegende Spezifikation für die Präzision der Bohrlochpositionierung. OPMT 5-Achs-Bohrplattformen erreichen eine Wiederholgenauigkeit von ±0,005 mm durch integrierte, geschlossene Positioniersysteme. Heidenhain Linearglasmaßstäbe – Standardausstattung im gesamten Produktportfolio – liefern Positionsrückmeldung in Echtzeit mit einer Auflösung von 1 Mikrometer. Dadurch können Servoregelungsalgorithmen thermische Ausdehnung, mechanische Durchbiegung und Positionierfehler, die Kugelgewindetrieben inhärent sind, kompensieren.
Die Spezifikationen für die Positionierung der Drehachse bestimmen die Winkelgenauigkeit beim Bohren von komplexen Winkeln. Toleranzen von ±10 Bogensekunden für die B- und C-Achse entsprechen linearen Positionsfehlern von unter 0,005 mm bei typischen Arbeitsabständen vom Drehzentrum. Diese Winkelgenauigkeit gewährleistet, dass die Anstellwinkel des Bohrers innerhalb der Spezifikationen bleiben, die die Rechtwinkligkeit des Bohrlochs und die Ausrichtung der Mittellinie beeinflussen – kritische Parameter beim Bohren von sich kreuzenden Löchern oder beim Erstellen präziser komplexer Winkelstrukturen.
Die Spezifikationen zur Wiederholgenauigkeit unterscheiden zwischen zufälligen Positionsabweichungen und systematischen Genauigkeitsfehlern. OPMT-Systeme weisen eine Wiederholgenauigkeit von ±0,003 mm über die linearen Achsen auf, was bedeutet, dass sie trotz Temperaturschwankungen, Achsenbelastungen und Betriebsdauer zuverlässig in die Sollposition zurückkehren. Diese hohe Wiederholgenauigkeit ermöglicht eine statistische Prozesskontrolle, bei der die Lochpositionsverteilungen innerhalb der Toleranzbereiche bleiben. Dadurch werden die Produktionsausbeuten maximiert und gleichzeitig der Prüfaufwand minimiert.
Schnelle Verfahrgeschwindigkeiten ermöglichen eine hohe Grundproduktivität durch optimierte, nicht schneidende Bewegungen. Achsengeschwindigkeiten von 30–48 m/min minimieren die für die Positionierung zwischen den Bohrungspositionen benötigte Zeit und reduzieren die Zykluszeiten proportional zur Bohrungsdichte. Bei Bauteilen mit mehr als 100 Bohrungen auf einer Fläche von 500 mm × 500 mm reduziert die Optimierung der schnellen Verfahrgeschwindigkeit die Gesamtzykluszeit um 15–251 TP3T im Vergleich zu Systemen mit herkömmlichen Verfahrgeschwindigkeiten von 24 m/min.
Die Schnittvorschubgeschwindigkeit optimiert das Verhältnis zwischen Materialabtrag und Bohrlochqualität. Die optimale Bohrgeschwindigkeit liegt je nach Materialhärte, Bohrlochdurchmesser und Oberflächengüte zwischen 5 und 20 m/min. Die adaptive Vorschubregelung passt die Schnittgeschwindigkeit in Echtzeit anhand der Schnittkraft an und gewährleistet so optimale Spanabfuhrbedingungen während des gesamten Bohrvorgangs. Diese dynamische Optimierung verlängert die Werkzeugstandzeit um 25–401 TP3T und verhindert gleichzeitig die Verschlechterung der Bohrlochqualität, die bei konstanter Vorschubgeschwindigkeit in Verbindung mit Materialhärteschwankungen oder unterbrochenen Schnittbedingungen auftreten kann.
Die Werkzeugwechselzeiten beeinflussen die Gesamtanlageneffektivität bei Anwendungen mit unterschiedlichen Bohrdurchmessern. Werkzeugwechsel in acht Sekunden ermöglichen die effiziente Bearbeitung von Bauteilen mit verschiedenen Bohrungsdurchmessern, während Magazinkapazitäten für 30 Werkzeuge manuelle Werkzeugladevorgänge überflüssig machen, die den Produktionsfluss sonst stören würden. Die kumulierten Zeiteinsparungen summieren sich über die Produktionsmenge und reduzieren den Werkzeugwechselaufwand von 201 TP3T der Gesamtzykluszeit auf unter 51 TP3T bei Bohrungen mit mehreren Durchmessern.
Die Bearbeitungsleistung bei extrem harten Materialien unterscheidet moderne 5-Achs-Plattformen von herkömmlichen Bearbeitungszentren. Erfolgreiche Bohrvorgänge in PCD- (Polykristalliner Diamantkompakt), PCBN- (Polykristallines Kubisches Bornitrid) und CVD-Diamantwerkstoffen (Chemische Gasphasenabscheidung) erfordern lasergestützte Verfahren, die mechanischen Werkzeugverschleiß und Schnittkraftbegrenzungen eliminieren. OPMT-Systeme bearbeiten diese Materialien routinemäßig und erreichen Lochdurchmesser von 0,1 mm bis 5 mm mit Tiefen-zu-Durchmesser-Verhältnissen von über 10:1.
Die Bearbeitung von Legierungen für die Luft- und Raumfahrt erweitert die Möglichkeiten auf Titan (Ti-6Al-4V), Nickelbasis-Superlegierungen (Inconel 718, Inconel 625) und Aluminium-Lithium-Verbundwerkstoffe. Diese schwer zerspanbaren Werkstoffe erfordern optimierte Schnittparameter, darunter spezielle Werkzeuggeometrien, Hochdruckkühlung und Tiefbohrzyklen zur Spankontrolle. Fünf-Achs-Bohrplattformen gewährleisten die Einhaltung der Spezifikationen für die Bohrungsqualität, einschließlich Positionsgenauigkeit innerhalb von ±0,01 mm, Rechtwinkligkeit innerhalb von ±0,005 mm und Oberflächenrauheit unter Ra 0,8 μm für diese anspruchsvollen Werkstoffkategorien.
Das Bohren von Keramikverbundwerkstoffen stellt die größte Herausforderung in der Materialbearbeitung dar. Zirkonoxid-Biokeramiken, Siliziumkarbid-Verbundwerkstoffe und Aluminiumoxid-Strukturkeramiken weisen Sprödigkeit auf, die unter zu hoher mechanischer Belastung beim Bohren zu katastrophalen Brüchen führt. Wassergeführtes Laserbohren eliminiert mechanische Spannungskonzentrationen und ermöglicht so präzise Bohrungen in Keramikbauteilen ohne Mikrorisse, die die strukturelle Integrität beeinträchtigen. Die Anwendungsbereiche reichen von medizinischen Implantaten über Halbleiterverarbeitungsanlagen bis hin zu Keramikturbinenkomponenten für Luft- und Raumfahrtantriebssysteme.
Die Toleranzvorgaben für die Rundheit quantifizieren die Rundheit von Bohrungen – die Maßabweichung zwischen maximalem und minimalem Durchmesser, gemessen über einen beliebigen Querschnitt. Fünfachsige Bohrbearbeitungen erreichen eine Rundheit von unter 0,003 mm durch eine robuste Maschinenkonstruktion, präzise Spindellager und eine adaptive Prozesssteuerung, die Vibrationseinflüsse minimiert. Diese Maßgenauigkeit ist entscheidend für Presspassungen von Lagern, präzise Stiftausrichtungen und Flüssigkeitsdichtungen, da Unrundheiten Montageprobleme oder Betriebsstörungen verursachen können.
Die Rechtwinkligkeitstoleranz definiert das Winkelverhältnis zwischen Bohrungsmittellinien und Bezugsflächen. OPMT-Bohrsysteme gewährleisten eine Rechtwinkligkeit von ±0,005 mm über eine Bohrungstiefe von 25 mm und somit die korrekte Montage und Funktion von Bauteilen in Anwendungen, bei denen Winkelabweichungen die Leistung beeinträchtigen. Anwendungen wie Kühlbohrungen für Turbinenschaufeln, Drainagekanäle für medizinische Implantate und Präzisionswerkzeuge stellen hohe Anforderungen an die Rechtwinkligkeit, die mit herkömmlichen Bohranlagen bei großen Produktionsvolumina nicht zuverlässig erfüllt werden können.
Spezifikationen für die Oberflächenbeschaffenheit legen die Qualität der Bohrlochwand anhand von Ra-Messungen (mittlere Rauheit) fest. Mechanische Bohrverfahren erreichen typischerweise Ra-Werte von 0,8–1,6 µm, abhängig von den Materialeigenschaften und Schnittparametern. Laserbearbeitungsverfahren reduzieren die Oberflächenrauheit auf Ra 0,2–0,4 µm und beseitigen gleichzeitig Grate, Umwandlungsschichten und Mikrorisse, welche die Dauerfestigkeit und Korrosionsbeständigkeit beeinträchtigen. Anwendungen in der Medizintechnik und in Strukturbauteilen der Luft- und Raumfahrt profitieren gleichermaßen von einer verbesserten Oberflächenintegrität, die die Lebensdauer der Bauteile verlängert.
Ein direkter Kostenvergleich mit dem EDM-Bohren (Funkenerosion) verdeutlicht die wirtschaftlichen Vorteile. Fünfachsige mechanische und Laserbohrverfahren erzielen eine Kostenreduzierung von 60% pro Bohrung durch den Wegfall der Herstellung von Verbrauchsmaterialien für Elektroden, verkürzte Bearbeitungszeiten und geringeren Energieverbrauch. Die Zykluszeitverbesserungen von 200% ermöglichen eine Verdopplung des Durchsatzes bei gleichbleibender Anlagenfläche, während der Wartungsaufwand durch den Wegfall des Elektrodenverschleißes beim EDM-Verfahren und des notwendigen Dielektrikummanagements sinkt.
Die Spezifikationen zum Energieverbrauch belegen die Kostenvorteile im Betrieb. OPMT 5-Achs-Bohrzentren verbrauchen 22 kWh pro 8-Stunden-Schicht, verglichen mit 35 kWh bei gleicher EDM-Kapazität. Die Energieeinsparung des 37% summiert sich über die gesamte Jahresproduktion und führt zu messbaren Einsparungen bei den Energiekosten, während gleichzeitig die Nachhaltigkeitsinitiativen des Unternehmens unterstützt werden. Weitere Umweltvorteile sind der Wegfall der Entsorgung von Dielektrikum, ein reduzierter Kühlschmierstoffverbrauch und weniger Ausschuss durch höhere Ausbeute beim ersten Durchgang.
Die Optimierung der Werkzeugstandzeit trägt durch geringere Verbrauchskosten zu kontinuierlichen Kostensenkungen bei. Optimierte Schnittgeometrie, adaptive Vorschubsteuerung und Hochdruckkühlung verlängern die Standzeit von Hartmetallbohrern im Vergleich zu herkömmlichen Bohrverfahren um 25 bis 401 TTP3T. Diese Verbesserungen der Standzeit reduzieren die Werkzeugbeschaffungskosten, minimieren Werkzeugwechsel und verringern die Ausfallzeiten, die in der Serienfertigung durch Werkzeugwechsel entstehen.
Strategische Investitionsentscheidungen im Bereich Anlagentechnik erfordern eine umfassende Analyse der Gesamtbetriebskosten, der Implementierungsanforderungen und der prognostizierten Kapitalrendite (ROI) über die erwarteten Produktionsvolumina hinweg. Das folgende Rahmenwerk legt Kriterien für die finanzielle Bewertung, Aspekte der Anlagenintegration und Anforderungen an die operative Unterstützung fest, die Fertigungsunternehmen bei der Implementierung von 5-Achs-Bohrsystemen berücksichtigen.
Die anfängliche Investitionskosten für 5-Achs-Bohrzentren liegen je nach Maschinenkonfiguration, Automatisierungsintegration und anwendungsspezifischen Anpassungsanforderungen zwischen 250.000 und 850.000 TP4T. Diese Anschaffungskosten bilden die Grundlage für die Berechnung der Kapitalrendite, bei der die Anschaffungskosten den durch die Implementierung erzielten Betriebskostensenkungen und Produktivitätssteigerungen gegenübergestellt werden.
Die Modellierung zur Reduzierung der Betriebskosten prognostiziert gemäß 22-28% eine Senkung der gesamten Fertigungskosten innerhalb von drei Jahren für Unternehmen, die jährlich mehr als 10.000 Bauteile fertigen. Die Einsparungen resultieren aus mehreren Faktoren: reduzierter Rüstaufwand durch Bohrvorgänge in einer einzigen Aufspannung, geringere Ausschussquoten durch verbesserte Erstbearbeitungsqualität, niedrigerer Werkzeugverbrauch durch optimierte Schnittparameter und minimierte Nachbearbeitungskosten durch präzise Bohrungsplatzierung. Unternehmen dokumentieren Amortisationszeiten von 18 bis 36 Monaten, abhängig von Produktionsvolumen, Bauteilkomplexität und Fertigungseffizienz vor der Implementierung.
Produktivitätssteigerungen führen direkt zu einer Erhöhung der Umsatzkapazität. Einrichtungen, die implementieren 5-Achs-CNC-Bearbeitungszentren Durch die Optimierung der Bohrprozesse wird eine Zykluszeitverkürzung von 40–701 TP3T bei komplexen Bauteilen erreicht. Dies ermöglicht Produktionssteigerungen ohne proportionale Anlagenerweiterung oder Personalaufstockung. Die verbesserte Durchsatzleistung unterstützt Wachstumsinitiativen, die Reaktion auf steigende Nachfrage und die Erschließung von Marktanteilen, die mit den bestehenden Kapazitätsgrenzen nicht realisierbar gewesen wären.
Die Integration von CAM-Software (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) etabliert den digitalen Workflow, der die Bauteilkonstruktion mit der Bearbeitungsausführung verbindet. Moderne CAM-Plattformen wie Mastercam, Siemens NX und Dassault CATIA bieten native 5-Achs-Bohrmodule, die optimierte Werkzeugwege aus CAD-Modellen generieren. Der Programmier-Workflow ermöglicht es den Entwicklungsteams, Bohrvorgänge zu simulieren, Kollisionen zu vermeiden und die Bohrlochpositionen zu validieren, bevor die Programme an die Produktionsanlagen übertragen werden.
Die automatisierte Werkzeugweggenerierung reduziert die Programmierzeit im Vergleich zur manuellen G-Code-Entwicklung um 60–751 Tsd. Minuten. CAM-Systeme erkennen Bohrungsmerkmale in CAD-Modellen, wählen automatisch die passenden Bohrergrößen aus, berechnen die Anstellwinkel und generieren Bewegungsbefehle, die die Zykluszeit optimieren und gleichzeitig die Qualitätsvorgaben einhalten. Diese Automatisierung demokratisiert die 5-Achs-Programmierung und senkt die Hürde des spezialisierten Fachwissens, die die Einführung der 5-Achs-Technologie bisher auf Unternehmen mit erfahrenen CNC-Programmierern beschränkte.
Die Schulungsanforderungen für den Übergang von 3-Achs- zu 5-Achs-Systemen erweisen sich als weniger anspruchsvoll als bisher angenommen. Bediener mit Erfahrung in der konventionellen CNC-Bearbeitung erreichen in der Regel innerhalb von 2–3 Wochen durch strukturierte Schulungsprogramme einen produktiven 5-Achs-Betrieb. OPMT bietet umfassende Bedienerschulungen an, die Maschineneinrichtung, Programmladen, Werkzeugmanagement und Qualitätsprüfungsverfahren abdecken. Weiterführende Schulungen behandeln CAM-Programmierung, Prozessoptimierung und Fehlerbehebungsverfahren zur Maximierung der Anlagenauslastung.
Die Flächenaufteilung berücksichtigt die Maschinenstellfläche sowie die Zugangswege für Werkzeugladung, Werkstückhandhabung und Wartungsarbeiten. Standardmäßige OPMT 5-Achs-Bohrplattformen benötigen je nach Modellkonfiguration 15–25 m², zuzüglich Fläche für Späneabsaugung, Kühlmittelbehälter und Hilfseinrichtungen. Bei der Optimierung des Anlagenlayouts werden Materialflussmuster, die Nähe der Qualitätsprüfstationen und die Integration mit vor- und nachgelagerten Fertigungsprozessen berücksichtigt.
Die Spezifikationen für die Druckluftversorgung legen die Anforderungen an pneumatische Systeme für den automatisierten Werkzeugwechsel, die Werkstückspannung und die Späneabfuhr fest. Die Systeme benötigen einen Versorgungsdruck von 0,7 MPa und Fördermengen von 300 bis 500 Litern pro Minute, abhängig vom Maschinenmodell und Automatisierungsgrad. Die Spezifikationen für die Luftqualität schreiben eine Filtration bis 5 Mikrometer mit einem Taupunkt unter -20 °C vor, um Kondensation zu verhindern, die die Zuverlässigkeit der pneumatischen Komponenten beeinträchtigen könnte.
Die Anforderungen an die elektrische Kapazität umfassen den Stromverbrauch der Werkzeugmaschine sowie der Hilfssysteme wie Kühlmittelpumpen, Späneförderer und die Beleuchtung der Anlage. Standardinstallationen benötigen einen 23-kVA-Drehstromanschluss mit 380 V ±101 V T3T und einer den örtlichen Elektrovorschriften entsprechenden Erdung. Die Anforderungen an die Stromqualität betreffen Spannungsstabilität, Oberschwingungsgrenzen und Überspannungsschutz, um einen gleichbleibenden Maschinenbetrieb zu gewährleisten und empfindliche elektronische Steuerungskomponenten zu schützen.
Die Laserinterferometrie-Verifizierung legt Genauigkeitsvorgaben für Maschinen durch umfassende Positionsprüfungen über alle Achsen hinweg fest. Diese Präzisionsmesssysteme – mit einer Genauigkeit von ±0,5 Mikrometern – vergleichen die tatsächlichen Maschinenpositionen mit den Sollkoordinaten und quantifizieren so Positionierungsfehler, die die Genauigkeit der Bohrungspositionierung beeinträchtigen. Die Erstabnahmeprüfung dokumentiert die Leistungsfähigkeit der Maschine, während die jährliche Nachprüfung Genauigkeitsverschlechterungen aufdeckt, die eine mechanische Justierung oder den Austausch von Komponenten erfordern.
Die Prüfprotokolle für die Kugelstange bewerten die Maschinenleistung bei simultaner Mehrachsenbewegung – dem für 5-Achs-Bohrvorgänge relevantesten Betriebsmodus. Das Kugelstangenmesssystem erkennt geometrische Fehler wie Achsenabweichungen, Umkehrspitzen und Servo-Fehlanpassungen, die die Bohrlochqualität beim Bohren mit komplexem Winkel beeinträchtigen. Regelmäßige Kugelstangenprüfungen (empfohlen vierteljährlich) identifizieren sich anbahnende Probleme, bevor sie die Produktionsqualität beeinträchtigen, und ermöglichen so eine vorausschauende Wartung, die teuren Ausschuss verhindert.
Vorbeugende Wartungspläne optimieren die Anlagenzuverlässigkeit durch systematische Inspektion und Wartung. Tägliche Kontrollen durch den Bediener überprüfen Kühlmittelstand, Funktion des Schmiersystems und ausreichenden Luftdruck. Die wöchentliche Wartung umfasst Spindelreinigung, Schmierung der Führungsbahnen und Inspektion des Späneförderers. Vierteljährliche Wartungsintervalle beinhalten die Inspektion der Kugelgewindespindel, die Zustandsbewertung der Führungsschienen und die Präzisionskalibrierung. Die Wartungsprogramme von OPMT bieten detaillierte Checklisten, Spezifikationen für Ersatzteile und technischen Support, um die Maschinenverfügbarkeit über mehrere Jahre hinweg zu maximieren.
Die Inbetriebnahmeservices von OPMT gewährleisten die korrekte Maschineneinrichtung durch systematische Überprüfung der mechanischen Montage, der elektrischen Anschlüsse und der Konfiguration des Steuerungssystems. Die Servicetechniker von OPMT führen umfassende Maschinentests durch, einschließlich Achsenkalibrierung, Spindelprüfung und Validierung der Drehachsenpositionierung. Der Inbetriebnahmeprozess dauert in der Regel 3–5 Tage vor Ort und schließt mit einer formellen Abnahmeprüfung ab, die die Maschinenleistung anhand der veröffentlichten Spezifikationen dokumentiert.
Die Bedienerschulungen vermitteln das notwendige Wissen für eine produktive Maschinennutzung. Die Standardschulung dauert 5 Tage und umfasst die Inbetriebnahme der Maschine, das Laden und Ausführen von Programmen, Werkzeugmanagementprotokolle, Werkstückeinrichtungsmethoden und grundlegende Fehlerbehebung. Weiterführende Schulungen behandeln CAM-Programmierung, Strategien zur Prozessoptimierung und Verfahren zur Qualitätsprüfung. Die Schulungen finden je nach Projektlogistik und Gruppengröße entweder in den OPMT-Einrichtungen oder beim Kunden vor Ort statt.
Kontinuierlicher technischer Support gewährleistet die Produktionskontinuität durch schnelle Problemlösung. Die Supportinfrastruktur von OPMT umfasst telefonischen Support während der Geschäftszeiten, Ferndiagnose zur Fehlerbehebung im Steuerungssystem und eine schnelle Ersatzteilversorgung, die die Verfügbarkeit von Komponenten innerhalb von 48–72 Stunden sicherstellt. Jährliche Serviceverträge beinhalten vorbeugende Wartungsbesuche, bevorzugten Zugriff auf Ersatzteile und eine umfassende Garantieabdeckung, die Ihre Investitionen in die Anlagen über mehrere Betriebsjahre hinweg schützt.
5-Achs-CNC-Bearbeitungszentren für Bohrungen revolutionieren die Präzisionsbohrungsbearbeitung durch geometrische Freiheit, Positioniergenauigkeit und Prozessintegration, die mit herkömmlichen Bohranlagen nicht zu erreichen sind. Fertigungsunternehmen, die Komponenten für Luft- und Raumfahrtturbinen, Implantate für medizinische Geräte, Elektrofahrzeuge, Ölbohranlagen und Präzisionsschneidwerkzeuge bearbeiten, erzielen messbare Vorteile, darunter eine Reduzierung der Zykluszeit um 40–701 TP3T, eine Verbesserung der Positioniergenauigkeit um 681 TP3T und Kosteneinsparungen um 601 TP3T im Vergleich zu alternativen Bohrverfahren.
Die technischen Möglichkeiten gehen weit über einfache Produktivitätssteigerungen hinaus. Bohrvorgänge in einer einzigen Aufspannung eliminieren Toleranzfehler, die die Passgenauigkeit und Bauteilfunktion beeinträchtigen. Der Zugang für Bohrungen unter verschiedenen Winkeln ermöglicht Designoptimierungen, die mit herkömmlichen Fertigungsmethoden nicht realisierbar wären. Lasergestütztes Bohren in superharten Werkstoffen eröffnet Anwendungsbereiche, die bisher als wirtschaftlich unrentabel oder technisch unmöglich galten.
Das umfassende Portfolio an Bohrlösungen von OPMT deckt mit anwendungsoptimierten Plattformen vielfältige Fertigungsanforderungen ab. Die Light 5X 40V ermöglicht die präzise Werkzeugherstellung mit Femtosekundenlaser-Integration. Die 563V skaliert die Kapazität für große Bauteile der Luft- und Raumfahrt sowie der Automobilindustrie, die umfangreiche Lochmuster über große Arbeitsbereiche erfordern. Die revolutionäre WJC532V nutzt wassergeführte Lasertechnologie und erreicht Tiefen-Breiten-Verhältnisse von 100:1 in Keramikverbundwerkstoffen und polykristallinen Diamantwerkstoffen.
Für eine erfolgreiche Implementierung ist eine systematische Bewertung der Anlagenanforderungen, der Programmierkapazitäten und der Infrastruktur für den operativen Support erforderlich. Organisationen, die eine umfassende Gesamtkostenanalyse durchführen – unter Einbeziehung von Anschaffungskosten, Produktivitätssteigerungen, Qualitätsverbesserungen und betrieblichen Einsparungen –, dokumentieren regelmäßig einen Return on Investment innerhalb von 18 bis 36 Monaten bei Anwendungen mit hohem Bohrvolumen.
Bei der Bewertung von Präzisionsbohrlösungen durch Entscheidungsträger in der Fertigungsindustrie sollten Gerätedemonstrationen, die repräsentative Bauteilmaterialien verarbeiten, eine umfassende Bewertung der Programmierfähigkeit sowie detaillierte Gespräche über anwendungsspezifische Anpassungsanforderungen Priorität haben. Kontaktieren Sie OPMT Laser um technische Beratungen, Werksbesichtigungen und Prozessvalidierungsversuche zu vereinbaren, die die Fähigkeiten des 5-Achs-Bohrverfahrens im Hinblick auf spezifische Herausforderungen in der Fertigung demonstrieren.
Fünfachsige CNC-Bearbeitungszentren bieten bahnbrechende Vorteile für Präzisionsbohrarbeiten durch simultane Mehrachsen-Bewegungssteuerung, die die grundlegenden Einschränkungen herkömmlicher Dreiachsmaschinen beseitigt. Der Hauptvorteil zeigt sich in der Möglichkeit, Winkelbohrungen in einer einzigen Aufspannung durchzuführen: Fünfachsige Systeme erledigen alle Bohrungsvorgänge ohne Werkstückumpositionierung und eliminieren so die Toleranzfehler, die beim Umspannen von Bauteilen zwischen verschiedenen Vorrichtungen entstehen.
Dieses Verfahren mit einem einzigen Bezugspunkt reduziert die Werkstückhandhabungsfehler um 681 TP3T und gewährleistet gleichzeitig konsistente Bezugsflächen über alle Bearbeitungsschritte hinweg. Komplexe Bauteile mit Bohrungen in unterschiedlichen Winkeln – wie beispielsweise Turbinenschaufeln für die Luft- und Raumfahrt mit Kühlkanälen, medizinische Implantate mit Entwässerungskanälen oder Batterieträger für Kraftfahrzeuge mit Belüftungsmustern – werden in kontinuierlichen Bearbeitungszyklen bearbeitet, anstatt in mehrstufigen Sequenzen, deren Rüstzeit allein 2–4 Stunden in Anspruch nimmt.
Die Winkelzugänglichkeit ermöglicht echtes Mehrwinkelbohren, bei dem die Bohrlochmittellinien die Werkstückoberflächen in präzisen, nicht senkrechten Winkeln schneiden. Die Rotationsachsensteuerung (B-Achse -120° bis +30°, C-Achse 360°) positioniert die Bohrspindeln unabhängig vom Oberflächenwinkel optimal für jedes Bohrloch und erreicht so eine Rechtwinkligkeitstoleranz von ±0,005 mm über eine Bohrtiefe von 25 mm. Herkömmliche 3-Achs-Maschinen benötigen aufwendige Spannvorrichtungen, um die Oberflächen senkrecht zum Bohrwinkel auszurichten – jede dieser Vorrichtungen führt zu Positionierungsfehlern, die die Genauigkeit des Endbohrlochs beeinträchtigen.
Die Möglichkeit, sich kreuzende Bohrungen in präzisen Winkeln durchzuführen, erweist sich als besonders wertvoll für die Fertigung von Verteilerblöcken, Hydraulikkomponenten und Kühlsystemen. Die Fünf-Achs-Positionierung gewährleistet eine Ausrichtung der Mittellinie, die mit Vorrichtungen nicht erreichbar ist, und sichert so optimale Strömungseigenschaften und Druckverteilung in den montierten Systemen.
Moderne 5-Achs-Bearbeitungszentren mit integrierten Laserbearbeitungssystemen bohren präzise Löcher in extrem harte Werkstoffe wie PCD (Polykristalliner Diamantkompakt), PCBN (Polykristallines kubisches Bornitrid), CVD-Diamant (Chemische Gasphasenabscheidung) und Keramikverbundwerkstoffe. Diese Werkstoffe – gekennzeichnet durch eine extreme Härte, die die Leistungsfähigkeit herkömmlicher Schneidwerkzeuge übersteigt – erfordern lasergestützte Bohrtechniken, die den mechanischen Werkzeugverschleiß und die bei traditionellen Bohrverfahren üblichen Schnittkraftbegrenzungen eliminieren.
Femtosekunden-Lasersysteme Die in 5-Achs-Plattformen integrierten Verfahren ermöglichen ultrakurze Pulsdauern (10⁻¹⁵ Sekunden) zur Materialabtragung durch Kaltablation. Dieser fortschrittliche Mechanismus verdampft das Substratmaterial auf atomarer Ebene, ohne die umliegenden Bereiche thermisch zu belasten. Dadurch werden Wärmeeinflusszonen und Mikrorisse vermieden, die die strukturelle Integrität bei der Bearbeitung spröder Materialien beeinträchtigen. Das technische Ergebnis: Präzisionsbohrungen mit einer Positionsgenauigkeit von ±3 μm bei gleichzeitigem Erhalt der Materialeigenschaften über den gesamten Bohrlochumfang.
Die wassergeführte Lasertechnologie erweitert diese Möglichkeiten durch revolutionäre Strategien zur Partikelabfuhr und Wärmeregulierung. Hochdruckwasserstrahlen – geformt durch spezielle Düsengeometrien – lenken gleichzeitig die Laserenergie, entfernen abgetragene Partikel und führen die Restwärme während des gesamten Bohrvorgangs ab. Dieser integrierte Ansatz erzielt außergewöhnliche Tiefen-Breiten-Verhältnisse von 100:1 bei gleichzeitiger Aufrechterhaltung einer Positioniergenauigkeit von ±3 μm selbst bei Materialien, die unter herkömmlichen mechanischen Bohrkräften brechen würden.
Hybridbohrverfahren kombinieren die Effizienz des mechanischen Vorbohrens mit der Präzision der Laserbearbeitung, um sowohl die Produktivität als auch die Oberflächenqualität zu optimieren. Hartmetallbohrer tragen Material bis zu den Endabmessungen (90–951 µm) ab. Anschließend erfolgt die Laserbearbeitung, die Oberflächenrauheiten unter Ra 0,2 µm erreicht. Dieses zweistufige Verfahren vereint die Wirtschaftlichkeit des mechanischen Bohrens mit der hohen Qualität der modernen Laserbearbeitung – besonders vorteilhaft beim Bohren von Titanlegierungen, Inconel-Superlegierungen und Keramikmatrix-Verbundwerkstoffen, die in der Luft- und Raumfahrt sowie in der Medizintechnik eingesetzt werden.
Die 5-Achs-Bohrsysteme von OPMT erzielen dank integrierter Regelungssysteme mit geschlossenem Regelkreis eine außergewöhnliche Positioniergenauigkeit, die auch bei simultanen Mehrachsenbewegungen höchste Präzision gewährleistet. Die Linearachsen (X, Y, Z) bieten eine Wiederholgenauigkeit von ±0,005 mm, die durch eine lineare Glasmessskala von Heidenhain mit einer Auflösung von 1 Mikrometer verifiziert wurde. Diese Positioniergenauigkeit garantiert, dass die Bohrungspositionen unabhängig von der Werkstückposition innerhalb des Arbeitsbereichs der Maschine innerhalb der vorgegebenen Toleranzen bleiben.
Die Genauigkeitsvorgaben der Drehachse bestimmen direkt die Präzision beim Winkelbohren. Positioniertoleranzen der B- und C-Achse von ±10 Bogensekunden – entsprechend ±0,00028 Grad – führen zu linearen Positionsabweichungen von unter 0,005 mm bei typischen Arbeitsabständen von 100 mm vom Drehzentrum. Diese Winkelgenauigkeit gewährleistet, dass die Anstellwinkel des Bohrers innerhalb der Spezifikationen liegen, die die Rechtwinkligkeit des Bohrlochs, die Ausrichtung auf die Mittellinie und die Genauigkeit der Durchbruchposition bei komplexen Winkelbohrungen beeinflussen.
Die RTCP-Funktion (Rotation Tool Center Point) stellt den entscheidenden kinematischen Algorithmus bereit, der die Bohrgenauigkeit bei gleichzeitiger Rotation der Achsen gewährleistet. Dieses fortschrittliche Steuerungssystem berechnet die Positionskompensation in Echtzeit und hält so die Werkzeugspitze bzw. den Laserfokuspunkt trotz Änderungen der B- und C-Achsenorientierung relativ zur Werkstückoberfläche stationär. Beim Bohren von komplexen Winkelbohrungen, die eine Drehung des Werkstücks während des Vorgangs erfordern, sorgt RTCP für eine Genauigkeit der Bohrungsposition, die sich andernfalls durch unkompensierte Achsenbewegungen verschlechtern würde.
Echtzeit-Kompensationssysteme gleichen thermische Drift und Vibrationseffekte aus, die die Positioniergenauigkeit bei längeren Produktionsläufen beeinträchtigen. Temperatursensoren in den Maschinenkomponenten überwachen die Wärmeausdehnung und ermöglichen es den Regelalgorithmen, Positionskorrekturen vorzunehmen, die die Genauigkeit trotz Umgebungstemperaturschwankungen oder Wärmeentwicklung während der Bearbeitung gewährleisten. Hochfrequente Beschleunigungsmesser erkennen Vibrationsmuster, die auf beginnendes Rattern hinweisen, und lösen adaptive Reaktionen aus, die Vorschubgeschwindigkeit und Spindeldrehzahl anpassen, um stabile Bohrbedingungen wiederherzustellen.
Das praktische Ergebnis: Positionsgenauigkeit der Bohrungen innerhalb von ±0,005 mm, Rechtwinkligkeit innerhalb von ±0,005 mm über eine Tiefe von 25 mm und Präzision bei zusammengesetzten Winkeln innerhalb von ±10 Bogensekunden bei Produktionsvolumina von Tausenden von Bauteilen. Diese Leistungsmerkmale erfüllen die anspruchsvollen Spezifikationen für Turbinenkomponenten in der Luft- und Raumfahrt, Implantate für medizinische Geräte und Präzisionswerkzeuge, bei denen die Maßgenauigkeit die Bauteilleistung und die Einhaltung gesetzlicher Vorschriften direkt beeinflusst.
Haftungsausschluss
Dieser Inhalt wurde von OPMT Laser auf Grundlage öffentlich verfügbarer Informationen zusammengestellt und dient ausschließlich zu Referenzzwecken. Die Erwähnung von Marken und Produkten Dritter dient dem objektiven Vergleich und stellt keine kommerzielle Verbindung oder Billigung dar.
Entdecken Sie die Welt der CNC-Bearbeitung, indem wir 3-Achsen- und 5-Achsen-Technologien vergleichen. Von einfachen Vorgängen bis hin zu komplexen Geometrien – finden Sie heraus, welche Maschine Ihren Fertigungsanforderungen im Jahr 2025 entspricht.

Entdecken Sie OPMTs bewährten 5-Phasen-ODM-Prozess für kundenspezifische Lasersysteme. ISO-zertifizierte Fertigung, Präzision ±0,003 mm, IP-Schutz. Senden Sie uns noch heute Ihre Projektanforderungen.

Suchen Sie nach den besten Anbietern für 5-Achsen-CNC-Bearbeitungszentren? In unserer Top-10-Liste finden Sie Expertenwissen und die perfekte Lösung für Ihre Anforderungen!

Entdecken Sie die 10 besten Laser-Metallschneidmaschinen des Jahres 2025, darunter Branchenführer wie Trumpf, Bystronic und OPMT Laser. Vergleichen Sie Spitzentechnologie, Präzision und Effizienz, um die perfekte Lösung für Ihre Fertigungsanforderungen zu finden.
Bitte geben Sie Ihre Kontaktinformationen ein, um das PDF herunterzuladen.

