Programar una visita
Independientemente de si necesita asesoramiento general o apoyo específico, estaremos encantados de ayudarle.
Independientemente de si necesita asesoramiento general o apoyo específico, estaremos encantados de ayudarle.
Todas las noticias
Compartir
El mercado de equipos de marcado láser alcanzó los 1000 millones de dólares a nivel mundial en 2025, impulsado por los mandatos de trazabilidad automotriz, las regulaciones UDI de dispositivos médicos y los requisitos de serialización de la Industria 4.0. Sin embargo, seleccionar al proveedor adecuado implica mucho más que comparar hojas de especificaciones. Tras analizar más de 300 instalaciones de fabricación de proveedores automotrices de primer nivel, centros médicos regulados por la FDA y operaciones de ensamblaje de productos electrónicos de alto volumen, se observan patrones claros que distinguen los sistemas de marcado láser excepcionales de los simplemente adecuados.
Esta evaluación técnica examina a los 10 principales proveedores en función de tres factores críticos: desempeño de campo comprobado en entornos industriales exigentes, soporte integral de ingeniería de aplicaciones para el desarrollo de procesos e infraestructura de servicio a largo plazo que sustenta los equipos de producción durante ciclos de vida de 10 a 15 años.
Al ingresar a cualquier planta de estampación automotriz, se observarán de inmediato las limitaciones de los métodos de identificación mecánica: matrices dobladas, profundidades inconsistentes y acumulación de piezas rechazadas por sobreimpresión. El marcado láser eliminó estos tipos de fallo en las instalaciones de un proveedor de primer nivel en Michigan, reduciendo el desperdicio de 2100 PPM a 180 PPM, a la vez que se marca 47 segundos más rápido por conjunto de carcasa.
El principio fundamental aprovecha la energía fotónica concentrada para alterar permanentemente las superficies de los materiales. Tres longitudes de onda principales predominan en las aplicaciones industriales, cada una con diferentes mecanismos de absorción:
Láseres de fibra a 1064 nm Generan una longitud de onda infrarroja fuertemente absorbida por las nubes de electrones metálicos. Un láser de fibra de 50 W proporciona intensidades pico superiores a 10^6 W/cm², suficientes para vaporizar capas de material de 50-200 μm de profundidad en nanosegundos. El coeficiente de absorción del acero inoxidable de 0,35-0,45 a esta longitud de onda permite un marcado rápido: los códigos Data Matrix 2D típicos (10 mm x 10 mm) se completan en 0,8-1,2 segundos.
Láseres UV a 355 nm Emplean mecanismos fotoquímicos en lugar de puramente térmicos. La longitud de onda más corta rompe los enlaces moleculares directamente, creando lo que los científicos de materiales denominan "ablación fría". Esto es crucial para las placas de circuito FR-4, donde el daño térmico se propaga a través de las capas laminadas. Los sistemas UV se enfocan en puntos de 12-18 μm con zonas afectadas por el calor por debajo de los 20 μm, lo que previene la oxidación y la delaminación de las trazas de cobre que plagaron los intentos anteriores con láser de fibra en la electrónica.
Láseres de CO2 a 10,6 μm Modos de vibración molecular objetivo en materiales orgánicos y agua. La madera, el papel, la mayoría de los plásticos y el vidrio absorben eficientemente esta longitud de onda del infrarrojo lejano. Sin embargo, la física de longitudes de onda más largas limita el diámetro del foco a 100-200 μm, lo que limita la resolución para características finas. La eficiencia del conector de pared 10-20%, en comparación con el 40-50% para sistemas de fibra, impacta significativamente la economía operativa en la producción a gran escala.
Las hojas de datos de los equipos muestran cifras impresionantes, pero el rendimiento en campo suele contar historias diferentes. Tres parámetros predicen el éxito en la práctica mejor que la potencia nominal del láser:
Calidad del haz (factor M²): Esta métrica adimensional cuantifica la precisión de enfoque de un láser en comparación con los límites teóricos. Un M² de 1,3 significa que el punto de enfoque es 1,3 veces mayor que el ideal. Para el marcado de dispositivos médicos que requieren caracteres de 0,1 mm en instrumentos quirúrgicos, la diferencia entre M² = 1,3 y M² = 1,6 determina si las marcas siguen siendo legibles después de 100 ciclos de esterilización. IPG Photonics mantiene un M² <1,3 en toda su cartera de láseres de fibra, lo que explica por qué los fabricantes de equipos originales (OEM) médicos especifican sistemáticamente sistemas basados en IPG para la serialización de dispositivos implantables.
Precisión de posicionamiento del galvanómetro: La mayoría de los proveedores indican una repetibilidad de ±10 μm. La realidad depende de las condiciones ambientales, el historial de mantenimiento y la estabilidad térmica de la trayectoria del haz. Durante la calificación de una línea de envasado farmacéutico, medimos la desviación de posicionamiento real durante turnos de producción de 8 horas. Los sistemas con una gestión térmica inadecuada presentaron una variación de 28-35 μm, lo que provocó que las marcas de Grado C no superaran la verificación ISO/IEC 15415. Los sistemas con compensación de temperatura (Coherent PowerLine, TRUMPF TruMark 6000) mantuvieron una consistencia de ±4,5 μm incluso a 35 °C sin refrigeración por agua fría.
Estabilidad energética pulso a pulso: Los láseres de fibra generan pulsos individuales mediante conmutación Q o modulación. La variación de energía entre pulsos genera una profundidad y un contraste de marca desiguales. Los sistemas premium mantienen una estabilidad de ±2% (±1% para plataformas de grado médico), mientras que las unidades económicas presentan una variación de ±8-12%. Esto afecta directamente la producción a alta velocidad: con 50 000 marcas al día, la variación de 8% genera cientos de piezas fuera de especificaciones que requieren verificación manual.
Cuando el principal fabricante de teléfonos inteligentes de China necesitó triplicar su productividad en el marcado de PCB y reducir los defectos en 60%, especificó la serie Laser MARVEL de Han tras una evaluación competitiva frente a alternativas europeas y japonesas. La instalación resultante marca 3200 placas de circuito por hora con verificación de visión automatizada, un estándar que otros proveedores tuvieron dificultades para igualar durante las pruebas.
Fundada en 1996, Han's Laser ha evolucionado de proveedor regional de equipos a empresa de fotónica integrada verticalmente, que controla la fabricación de fuentes láser, la producción de escáneres y el desarrollo de sistemas de control. Su sede en Shenzhen ocupa una superficie de 2,3 millones de metros cuadrados con instalaciones de investigación especializadas que emplean a más de 2000 ingenieros en diseño óptico, ingeniería mecánica y desarrollo de procesos.
Diferenciadores técnicos:
La plataforma MARVEL incorpora escáneres galvanométricos patentados que logran una precisión de posicionamiento de 3,5 μm en campos de marcado de 600 mm x 350 mm, significativamente mayores que las configuraciones estándar de 300 mm x 300 mm de la competencia. Esto es importante en aplicaciones automotrices donde las ubicaciones de marcado varían en piezas fundidas de gran tamaño. Un proveedor de transmisiones de Detroit marca ocho ubicaciones por carcasa sin reposicionamiento, lo que reduce el tiempo de ciclo de 18 segundos (sistema de la competencia) a 11 segundos.
La integración vertical de Han permite una rápida personalización. Cuando un fabricante aeroespacial requirió marcado rotatorio de 5 ejes para la serialización de álabes de turbina, Han entregó el prototipo en 90 días, frente a los 6 meses que los proveedores europeos solicitaban. El sistema ahora procesa 400 álabes diariamente con verificación automatizada por CMM, lo que confirma una precisión posicional de ±8 μm en superficies tridimensionales complejas.
Solicitud exitosa:
Los fabricantes de electrónica 3C representan el 40% de la base instalada de Han. Las implementaciones típicas alcanzan entre el 35 y el 42% de aumento de rendimiento en comparación con los métodos anteriores, principalmente mediante configuraciones multicabezal y posicionamiento guiado por visión, eliminando la fijación manual. Una planta de Guangdong marca carcasas de aluminio para portátiles a una velocidad de 2400 unidades/hora utilizando sistemas de doble cabezal de 50 W con carga automática.
Infraestructura de servicio:
Más de 100 centros de servicio en Asia-Pacífico, Europa y Norteamérica ofrecen asistencia local. La ventaja clave: disponibilidad de piezas las 48 horas en las principales regiones de fabricación. Durante una crisis de producción en la planta de Tennessee de un proveedor automotriz (fallo del galvanómetro el viernes por la tarde), el centro de servicio de Han en Nashville instaló un escáner de repuesto el sábado por la mañana, lo que evitó una parada de producción de una semana.
La precisión de la ingeniería alemana se une a 95 años de experiencia en fabricación en la serie TruMark de TRUMPF. Pero lo que realmente distingue a TRUMPF es el soporte integral para la validación de procesos, esencial para los fabricantes de dispositivos médicos que cumplen con la norma 21 CFR Parte 11 de la FDA.
Un fabricante de implantes ortopédicos dedicó tres meses a validar el sistema láser de un competidor antes de descubrir problemas de consistencia de la marca durante las pruebas de vida útil acelerada. Los ingenieros de aplicaciones de TRUMPF completaron la documentación de IQ/OQ/PQ en seis semanas, y las muestras de titanio marcadas con láser superaron las pruebas de corrosión de 5000 horas sin degradación. La diferencia: décadas de experiencia en dispositivos médicos, plasmadas en parámetros de proceso validados.
Arquitectura técnica de la serie TruMark 6000:
TRUMPF fabrica sus propias fuentes láser de fibra, lo que permite controlar la calidad del haz y la estabilidad a largo plazo, algo que la competencia no puede igualar con fuentes de terceros. El sistema de visión integrado representa una innovación significativa: dos cámaras capturan simultáneamente la posición de la pieza y verifican la calidad de la marca, lo que crea un control de proceso de circuito cerrado. Los parámetros se ajustan automáticamente si el contraste de la marca cae por debajo de los umbrales de grado A de la norma ISO/IEC 15415.
Impacto en la práctica: Un proveedor de componentes de seguridad automotriz (módulos de control de airbags) logró una calidad de primera pasada del 99,71 TP3T, frente al 94,21 TP3T de su sistema anterior. La mejora de 5,5 puntos porcentuales eliminó las estaciones de retrabajo manuales y redujo los costes de mano de obra en 127.000 TP4T anuales.
Capacidades de marcado sobre la marcha:
La sincronización de la cinta transportadora de TRUMPF permite marcar piezas móviles a velocidades de hasta 3 m/s, crucial para líneas de envasado de alta velocidad. Un fabricante farmacéutico marca blísters a 450 unidades/minuto con verificación de código 2D integrada. El sistema rechaza automáticamente las tarjetas que no superan la prueba de legibilidad antes de entrar en el envase estéril, lo que garantiza el cumplimiento de la serialización 100% según la Directiva de Medicamentos Falsificados de la UE.
Plataforma en la nube TRUMPF.Oseon:
La monitorización remota y el mantenimiento predictivo mediante conectividad en la nube ofrecen visibilidad en tiempo real de instalaciones en múltiples ubicaciones. Un fabricante de dispositivos médicos con 14 sistemas TruMark en tres instalaciones utiliza Oseon para estandarizar parámetros, monitorizar la vida útil de los componentes y programar el mantenimiento de forma proactiva. El tiempo de actividad de los equipos aumentó de 91% a 97,5% en seis meses desde la implementación.
Contratamos ingenieros láser para programar nuestro sistema anterior. Con KEYENCE, los supervisores de producción se encargan de los cambios. Este comentario de un proveedor automotriz de segundo nivel captura la propuesta de valor fundamental de KEYENCE: experiencia en automatización industrial traducida en interfaces de usuario intuitivas.
La serie MD-X de KEYENCE prioriza la simplicidad operativa sin sacrificar el rendimiento técnico. La interfaz de pantalla táctil de 15 pulgadas utiliza programación gráfica: los operadores arrastran, sueltan y configuran patrones de marcado sin codificación de texto. El tiempo de capacitación se reduce de 40 horas (típico para sistemas convencionales) a 6-8 horas.
Impacto de la tecnología de enfoque automático:
La mayoría de los sistemas láser requieren un posicionamiento preciso del eje Z, lo cual resulta problemático para piezas irregulares. El enfoque automático motorizado de KEYENCE admite una variación de altura de ±50 mm, ajustando automáticamente el enfoque para una calidad de marca óptima. Un fabricante de productos electrónicos que marcaba disipadores de calor de aluminio (variación de altura de 12-18 mm debido a las tolerancias de fundición) eliminó el ajuste manual, reduciendo el tiempo de ciclo de 8,5 a 3,2 segundos y mejorando la consistencia de la marca.
Posicionamiento de visión integrada:
El MD-X1500 incorpora reconocimiento de piezas mediante cámara, lo que elimina los costosos accesorios personalizados. Los operadores colocan las piezas en una región definida; el sistema de visión localiza las características y ajusta las coordenadas de marcado automáticamente. Un taller que produce componentes médicos personalizados (más de 250 números de pieza al año) redujo los costos de accesorios de $85,000/año a $12,000/año, a la vez que mejoró la velocidad de cambio de 25 minutos a 4 minutos.
Datos de rendimiento de campo:
Los fabricantes de componentes automotrices informan de una reducción del tiempo de cambio con el 40% en comparación con los sistemas de la competencia, lo que impacta directamente en la rentabilidad de la producción de alta variedad. Una planta que produce 80 componentes de transmisión diferentes logra un cambio promedio de 18 segundos, incluyendo el cambio de accesorios y la carga de parámetros.
Modelo de servicio:
El enfoque de venta directa de KEYENCE garantiza una calidad constante de soporte técnico. Los ingenieros de aplicaciones desarrollan procesos in situ, a menudo dedicando varios días a optimizar parámetros para materiales y geometrías específicos. Este soporte integral justifica el precio premium de KEYENCE (normalmente entre 15 y 251 TP3T más que en sistemas comparables) para fabricantes que priorizan la simplicidad operativa.
IPG no fabrica sistemas de marcado completos; crea las fuentes láser de fibra que alimentan el 60% de equipos de marcado industrial en todo el mundo. Comprender la tecnología de IPG revela por qué ciertos sistemas de marcado superan a otros con especificaciones aparentemente idénticas.
Arquitectura del láser de fibra dopada con iterbio:
IPG fue pionero en la construcción de láseres de fibra óptica, donde el medio de ganancia (fibra dopada con iterbio) forma una guía de ondas óptica integral. Esto elimina las trayectorias de haz en espacio libre que requieren alineación periódica, un modo de fallo que afecta a los láseres de estado sólido basados en varillas. Los fabricantes de dispositivos médicos valoran especialmente esta estabilidad: los sistemas basados en IPG mantienen una variación de potencia de salida de ±1,5% durante 50 000 horas de funcionamiento sin necesidad de ajustes.
Flexibilidad de parámetros de pulso:
Las fuentes IPG ofrecen un ajuste de la duración del pulso de 4 a 200 nanosegundos, lo que permite la optimización específica del material. El marcado de aluminio se beneficia de pulsos más cortos (4-10 ns), lo que minimiza las zonas afectadas por el calor, mientras que el grabado profundo de acero utiliza pulsos más largos (80-120 ns) para una máxima eliminación de material. Esta flexibilidad explica por qué los integradores de sistemas OEM prefieren las fuentes IPG al crear plataformas específicas para cada aplicación.
Métricas de confiabilidad:
El tiempo medio entre fallos (MTBF) supera las 100.000 horas en entornos industriales controlados. En otras palabras: un sistema de marcado láser que funciona 16 horas al día, 250 días al año, funciona durante más de 13 años antes de tener que sustituir la fuente. El coste total de la vida útil favorece notablemente a los sistemas basados en IPG, a pesar de la mayor inversión inicial (20-30%) frente a las alternativas económicas que requieren sustituir la fuente cada 3-5 años.
Aplicaciones de dispositivos médicos:
La calidad ultraestable del haz de IPG (M² <1,3) permite alturas de caracteres de 0,1 mm en instrumentos quirúrgicos, preservando al mismo tiempo la resistencia a la fatiga. Estudios clínicos de validación demuestran que los implantes de titanio marcados con láser resisten 10 millones de ciclos de carga sin iniciar grietas, un rendimiento equivalente al de los controles sin marcar. Estos datos de validación respaldan las solicitudes 510(k) de la FDA para fabricantes de dispositivos ortopédicos que implementan el marcado directo de piezas.
Coherent (que incorpora a la antigua Rofin-Sinar) se distingue por el desarrollo de procesos validados para la fabricación regulada por la FDA. La plataforma ExactWeld ejemplifica este enfoque: paquetes de documentación completos que respaldan las presentaciones regulatorias, en lugar de manuales genéricos de equipos.
Software de marco láser:
Esta plataforma de control de procesos registra todos los parámetros de marcado (potencia del láser, velocidad de escaneo, frecuencia y posición del enfoque), creando registros de auditoría que cumplen con la norma FDA 21 CFR Parte 11. Cuando se producen desviaciones en el proceso, el sistema detecta automáticamente las fallas, rechaza las piezas afectadas y notifica al personal de calidad. Un fabricante de medicamentos inyectables utiliza esta funcionalidad para mantener la conformidad con la serialización 100% en 2300 millones de viales al año.
Bibliotecas de procesos específicos de materiales:
Coherent mantiene parámetros validados para más de 400 combinaciones de materiales y geometrías, desarrolladas mediante la colaboración con clientes. Cuando un fabricante de implantes espinales requirió el marcado en una aleación de cobalto-cromo (notoriamente difícil debido al endurecimiento por deformación), el equipo de aplicaciones de Coherent proporcionó parámetros precalificados que lograron marcas de Grado A sin agrietamiento superficial. Los sistemas de la competencia requirieron de 6 a 8 semanas de experimentación en el desarrollo de parámetros.
Integración de plataformas de múltiples longitudes de onda:
Las plataformas de control único admiten láseres de fibra (1064 nm), verde (532 nm) y UV (355 nm), lo que permite flexibilidad de materiales sin necesidad de reentrenamiento del operador. Un fabricante por contrato que produce componentes médicos de metal y polímero utiliza esta capacidad para procesar 180 números de pieza diferentes en siete líneas de producto con interfaces de programación estandarizadas.
Servicios de soporte de validación:
Los especialistas en asuntos regulatorios de Coherent proporcionan plantillas de protocolos IQ/OQ/PQ, documentación de evaluación de riesgos (ISO 14971) y guía de biocompatibilidad (ISO 10993). Este apoyo acelera la comercialización de dispositivos médicos, lo cual es especialmente valioso para pequeños fabricantes que carecen de experiencia regulatoria interna. Una empresa de instrumental quirúrgico redujo su plazo de validación de 16 a 9 semanas gracias a los completos paquetes de documentación de Coherent.
Cuando un fabricante alemán de herramientas automotrices necesitaba marcar códigos de serie en filos de corte de PCD recién rectificados, a micrómetros de la geometría de corte, los sistemas de marcado convencionales de 2 ejes no podían mantener la incidencia perpendicular del haz sobre los complejos contornos de la herramienta. La plataforma CNC de 5 ejes de OPMT Laser solucionó este problema integrando el marcado láser directamente en el flujo de trabajo de rectificado de precisión, reduciendo el tiempo de producción de 51 a 34 minutos y mejorando la precisión de posicionamiento de la marca de ±45 μm a ±8 μm.

Fundada en 2015, OPMT ha evolucionado rápidamente, pasando de ser un proveedor chino a convertirse en una empresa innovadora en tecnología, con 302 patentes, incluidas 62 patentes de invención que abarcan métodos avanzados de procesamiento láser. Su planta de fabricación de Foshan, de 50.000 m², produce más de 1.000 sistemas al año, con una creciente presencia internacional en los mercados de Norteamérica, Europa y Asia-Pacífico, que atiende a las industrias de herramientas de precisión, automoción, dispositivos médicos y fabricación de moldes.
Serie Light 5X: Arquitectura de procesamiento láser de 5 ejes
El centro de mecanizado láser vertical Light 5X 40V representa la plataforma insignia de OPMT, integrando inclinación de ±120° en el eje B y rotación continua en el eje C con posicionamiento lineal X/Y/Z. Esta configuración permite la función de PUNTO CENTRAL DE LA HERRAMIENTA ROTATORIO (RTCP), que mantiene el enfoque del láser perpendicular a superficies tridimensionales complejas durante el movimiento simultáneo en 5 ejes.

Las especificaciones técnicas demuestran una precisión de fabricación que rara vez se ve fuera de los equipos de producción de dispositivos médicos y herramientas de precisión:
Capacidades de integración de múltiples procesos
A diferencia de los sistemas de marcado convencionales limitados a la identificación de superficies, las plataformas OPMT combinan múltiples procesos láser en configuraciones únicas:
Producción de herramientas de corte PCD para la fabricación de electrónica 3C:
Un fabricante de herramientas de precisión que suministra servicios de mecanizado de carcasas de teléfonos inteligentes utiliza sistemas Light 5X para marcar con láser los números de serie de las herramientas inmediatamente después del rectificado de acabado de los filos de corte de PCD (diamante policristalino). El proceso integrado elimina la manipulación intermedia, lo que reduce la duración del ciclo de producción y mejora la consistencia dimensional.
El reto: Las herramientas de PCD presentan geometrías complejas, incluyendo ángulos de alivio, rompevirutas y preparación precisa de filos. Todo ello requiere marcas ubicadas a menos de 0,5 mm de los filos de corte sin comprometer la geometría del filo ni introducir concentraciones de tensión. Los sistemas convencionales de 2 ejes no pueden mantener una incidencia óptima del haz en estas superficies compuestas.
Solución de OPMT: La cinemática de 5 ejes ajusta automáticamente la orientación de la herramienta, manteniendo la incidencia perpendicular del láser durante los ciclos de marcado. El sistema procesa la geometría completa de la herramienta, incluyendo:
Impacto en la producción: los fabricantes de herramientas informan una reducción del tiempo de ciclo 40% en comparación con operaciones de rectificado y marcado separadas, mientras que la consistencia del posicionamiento de la marca mejora de ±45 μm (fijación manual) a ±8 μm (posicionamiento controlado por CNC).
Texturizado de superficies de moldes automotrices + Identificación:
Los fabricantes de moldes de inyección texturizan superficies tridimensionales complejas para componentes interiores de automóviles (molduras del salpicadero, paneles de las puertas, componentes de la consola central) y luego marcan con láser los códigos de identificación de las cavidades en la misma configuración. Esta integración elimina errores de alineación entre las operaciones de texturizado y marcado.
Una planta de fabricación de moldes en Guangdong, que procesa moldes para interiores de automóviles, redujo el tiempo total de proceso de 73 horas (operaciones separadas de texturizado, marcado e inspección) a 48 horas. Más importante aún, mejoró la consistencia dimensional entre las características texturizadas y las marcas de identificación, un factor crucial para que los sistemas automatizados de gestión de moldes lean códigos y seleccionen los parámetros de proceso adecuados.
El reto técnico consiste en mantener un enfoque láser constante en superficies de moldes curvas de 300 a 400 mm con variaciones de altura superiores a 50 mm. El sistema de 5 ejes de OPMT, con cámara CCD integrada y sonda MP250, mide automáticamente la topología de la superficie, genera trayectorias de herramienta compensadas y ejecuta programas combinados de texturizado y marcado sin intervención del operador.
Marcado de componentes de dispositivos médicos:
Los fabricantes por contrato que producen instrumental quirúrgico y componentes de dispositivos implantables utilizan sistemas OPMT para marcar geometrías complejas que requieren la conformidad con la UDI de la FDA. La capacidad de 5 ejes permite marcar mangos de instrumentos curvos, superficies de apoyo cóncavas y características de ejes cilíndricos, aplicaciones donde los sistemas convencionales de 2 ejes tienen dificultades para mantener las especificaciones de calidad de marcado.
Un fabricante de dispositivos médicos que marca instrumentos de prueba ortopédicos de titanio (utilizados durante cirugías para dimensionar pero no implantados) valida las marcas que sobreviven a más de 100 ciclos de autoclave mientras mantienen una legibilidad de Grado B según ISO/IEC 15415. El posicionamiento de 5 ejes garantiza la incidencia perpendicular del haz incluso en las características curvas del instrumento, lo que evita la distorsión del marcado angular que causa una degradación prematura de la marca.
Herramientas de precisión para ensamblaje de componentes electrónicos:
Los fabricantes de herramientas de ultraprecisión para encapsulado de semiconductores y equipos de ensamblaje de PCB utilizan plataformas OPMT para marcar características submilimétricas en componentes de herramientas de carburo y cerámica. Estas aplicaciones exigen una precisión de posicionamiento de 5 μm, alcanzable únicamente mediante sistemas de control de movimiento de calidad CNC.
Una aplicación marca códigos Data Matrix 2D de 0,5 mm x 0,5 mm en boquillas cerámicas (1,2 mm de diámetro) utilizadas en equipos de colocación de virutas. Los códigos codifican las especificaciones de la geometría de la boquilla, lo que permite que los sistemas automatizados de gestión de herramientas seleccionen las boquillas adecuadas para diferentes tamaños de componentes. El sistema de 5 ejes gira la boquilla cilíndrica, presentando una superficie de marcado óptima al láser, a la vez que mantiene la precisión del enfoque en toda la geometría curva.
Sistema de control CNC basado en NUM:
La colaboración de OPMT con NUM (especialista suizo en CNC) ofrece un control de movimiento de calidad industrial que admite hasta 32 ejes sincronizados, superando con creces las capacidades de los controladores de marcado láser habituales, limitados a la coordinación del galvanómetro X/Y. La arquitectura abierta permite la integración de automatización personalizada:
Software de herramientas de corte GTR:
El software CAM propietario de OPMT aborda específicamente los requisitos de fabricación de herramientas de precisión:
Soporte de ingeniería de aplicaciones:
La OPMT mantiene un Centro Provincial de Investigación en Tecnología de Ingeniería y un Laboratorio Conjunto de Procesamiento Láser Ultrarrápido en colaboración con el Instituto de Óptica de Changchun de la Academia China de Ciencias. Esta infraestructura de investigación facilita el desarrollo de procesos específicos para cada cliente, lo que resulta especialmente valioso para materiales o geometrías novedosas que carecen de parámetros establecidos.
Un fabricante de herramientas de precisión requería el procesamiento láser de femtosegundos de insertos de corte cerámicos de carburo de silicio, un material emergente para el mecanizado de alta velocidad de compuestos y aleaciones no ferrosas. El equipo de aplicaciones de OPMT desarrolló parámetros validados en 8 semanas, incluyendo una caracterización exhaustiva de la tasa de remoción de material y un análisis de la zona afectada por el calor. El proceso resultante alcanza una precisión de mecanizado de 0,003 mm con un daño subsuperficial inferior a 2 μm, cumpliendo así con los requisitos de calificación del material del cliente.
Especificaciones técnicas – Lámpara 5X 40V:
| Parámetro | Especificación | Método de verificación |
|---|---|---|
| Ejes lineales (X/Y/Z) | 400 mm x 250 mm x 300 mm de recorrido | Medición física |
| Ejes rotatorios | B: ±120°, C: 360° continuo | Codificador angular |
| Posicionamiento lineal | Precisión de ±3 μm, repetibilidad de ±3 μm | Interferómetro láser (ISO 230-2) |
| Posicionamiento rotatorio | ±5 segundos de arco (±1 repetición de segundo de arco) | Calibrador Renishaw XM-60 |
| Travesía rápida | 30 m/min (ejes X/Y/Z) | Medición cronometrada |
| Aceleración | 0,5 g (ejes lineales) | Verificación del acelerómetro |
| Potencia del láser | Fibra de 100 W (estándar) | Medidor de potencia Ophir |
| Rango de ancho de pulso | De femtosegundo a nanosegundo | Verificación del osciloscopio |
| Campo de marcado | Hasta 600 mm x 350 mm (con 5 ejes) | Medición de placa de rejilla |
| Peso de la máquina | 3.500 kilos | Medición de celdas de carga |
| Espacio en el piso | 1.700 mm x 1.900 mm (2.700 mm con accesorios) | Medición física |
Servicio y capacitación:
El soporte posterior a la instalación incluye una semana de capacitación del operador en el sitio con documentación técnica completa que cubre:
La creciente presencia de servicio de OPMT en América del Norte (establecida en 2023) brinda soporte local para la creciente base de clientes occidentales. Los diagnósticos remotos las 24 horas a través del acceso VPN permiten una rápida resolución de problemas, mientras que el inventario regional de repuestos garantiza la disponibilidad de componentes de 48 a 72 horas para equipos de producción críticos.
Certificaciones de calidad:
Posición en el mercado:
OPMT ocupa un nicho especializado que atiende a fabricantes que requieren la integración del marcado láser con operaciones de mecanizado multieje, texturizado de superficies o medición de precisión. Mientras que los proveedores de marcado premium (TRUMPF, Coherent) ofrecen un rendimiento de marcado independiente superior, las plataformas láser CNC de OPMT ofrecen capacidades multiproceso únicas que no están disponibles en los equipos convencionales.
Perfil típico del cliente: fabricantes de herramientas de precisión, talleres de moldes, fabricantes contratados de dispositivos médicos y proveedores de herramientas automotrices especializadas que producen geometrías complejas donde el marcado representa un paso en flujos de trabajo integrales de procesamiento láser.
Para los fabricantes que requieren la integración del marcado láser con el mecanizado de precisión o el procesamiento de geometrías complejas, las plataformas láser CNC de OPMT ofrecen capacidades que no están disponibles en los equipos de marcado estándar. Contacte con el equipo de ingeniería de aplicaciones de OPMT para el desarrollo de soluciones personalizadas: Soluciones de mecanizado láser de 5 ejes OPMT
FOBA se especializa en sistemas listos para producción, diseñados para entornos exigentes de fabricación de dispositivos farmacéuticos y médicos. Las plataformas de la Serie Y cuentan con carcasas selladas con clasificación IP54 que protegen los componentes ópticos de la humedad, las partículas y la contaminación química típica de las áreas de producción adyacentes a salas blancas.
Excelencia en serialización farmacéutica:
Cuando entraron en vigor los requisitos de serialización de la Ley de Seguridad de la Cadena de Suministro de Medicamentos de EE. UU. (DSCSA), los fabricantes farmacéuticos necesitaban sistemas de marcado láser con tiempos de ciclo de 0,5 segundos y verificación 100%. La arquitectura integrada de FOBA combina láser de fibra, eje rotatorio y lector de códigos 2D en plataformas compactas que se adaptan a las necesidades de las líneas de envasado existentes.
Un fabricante farmacéutico que marca tapones para viales inyectables procesa 1800 unidades/hora con verificación automatizada, rechazando cualquier tapón que no cumpla con la norma ISO/IEC 15415 Grado B de legibilidad mínima. El enclavamiento a prueba de fallos impide que las unidades defectuosas entren en las operaciones de llenado estéril, lo cual es fundamental para el cumplimiento de las auditorías de la FDA.
Sincronización del eje rotatorio:
Las platinas rotatorias de precisión de FOBA admiten piezas cilíndricas de 5 mm a 120 mm de diámetro con detección automática de diámetro y ajuste de parámetros. Los fabricantes de dispositivos médicos que marcan jeringas de acero inoxidable logran una precisión de marcado circunferencial de ±15 μm, esencial para la alineación de la escala graduada.
Experiencia en integración:
La fortaleza de FOBA reside en su integración llave en mano con los equipos de producción existentes. Los ingenieros proporcionan programación de PLC, enclavamiento de seguridad y documentación de validación como entregas estándar. Este enfoque integral explica el dominio de FOBA en aplicaciones farmacéuticas, donde la validación de equipos representa entre el 30 y el 401% del coste total del proyecto.
MECCO se ha consolidado en la industria aeroespacial y de defensa de Norteamérica gracias a su amplia experiencia en el cumplimiento de la norma MIL-STD-130N y a sus sistemas de calidad con certificación AS9100D. Cuando las empresas aeroespaciales requieren componentes fabricados por el proveedor con marcado directo de piezas, los sistemas MECCO aparecen en las listas de equipos aprobados con mayor frecuencia que las alternativas.
Plataforma SMARTmark para la industria aeroespacial:
La serie SMARTmark incorpora parámetros precalificados para aleaciones aeroespaciales, como titanio (Ti-6Al-4V), Inconel (superaleaciones a base de níquel) y aluminio (7075-T6, 2024-T3). Esto es importante porque los materiales aeroespaciales presentan ventanas de procesamiento estrechas: una energía láser excesiva causa microfisuras que comprometen la resistencia a la fatiga, mientras que una energía insuficiente produce el desvanecimiento de las marcas durante la exposición al servicio.
El laboratorio de pruebas de materiales de MECCO caracteriza la interacción del láser con los materiales suministrados por el cliente, desarrollando parámetros validados y proporcionando análisis metalúrgicos que respaldan las aprobaciones del comité de revisión de materiales. Este servicio reduce los plazos de calificación de 12 a 16 semanas (típico para el desarrollo interno) a 4 a 6 semanas.
Cumplimiento del marcado UID:
Los requisitos de Identificación Única (UID) del Departamento de Defensa exigen que los códigos Data Matrix 2D resistan décadas de servicio en campo, incluyendo entornos corrosivos, temperaturas extremas y abrasión mecánica. Los sistemas MECCO logran marcas que resisten 5000 horas de exposición a niebla salina (ASTM B117), manteniendo una legibilidad de Grado A, superando así los requisitos de la norma MIL-STD-130N.
Un fabricante de componentes aeroespaciales que suministra trenes de aterrizaje para aviones de combate marca componentes de titanio con códigos Data Matrix de 3 mm x 3 mm. Tras pruebas de vida útil aceleradas que simulan 20 años de operaciones en la cubierta de un portaaviones, las marcas siguen siendo legibles con escáneres comerciales estándar.
Software WinLase:
El software de control de MECCO ofrece bibliotecas de materiales completas, control estadístico de procesos y gestión de parámetros en red. Los fabricantes con múltiples instalaciones estandarizan los procesos de marcado en todas sus plantas de producción, garantizando una calidad constante independientemente de la ubicación.
La fortaleza de Gravotech reside en sus cabezales láser compactos e integrables, que permiten a fabricantes de maquinaria a medida y contratistas médicos incorporar el marcado láser en equipos de producción especializados. La serie modular FiberStar ofrece un montaje compatible con OEM, interfaces eléctricas simplificadas y kits de desarrollo de software que facilitan la integración personalizada.
Fabricación por contrato de dispositivos médicos:
Los fabricantes por contrato que producen entre 50 y 200 números de pieza de dispositivos médicos diferentes al mes requieren flexibilidad de marcado sin necesidad de una programación compleja. El enfoque de Gravotech utiliza archivos de parámetros específicos de cada pieza, que se cargan mediante escaneo de código de barras o búsqueda en bases de datos, lo que permite un cambio rápido entre productos que requieren diferentes ajustes del láser.
Un fabricante de instrumental quirúrgico por contrato marca más de 80 tipos de instrumentos con tiempos de carga inferiores a 90 segundos. El sistema recupera automáticamente los parámetros basándose en los números de pieza escaneados, eliminando así los errores de entrada manual de datos que anteriormente causaban tasas de retrabajo de 3-5%.
Ventajas del tamaño compacto:
El cabezal láser FiberStar mide 450 mm x 180 mm x 220 mm y pesa 18 kg, lo que permite el montaje robótico de efectores finales o su integración en celdas de ensamblaje multiestación. Los fabricantes de electrónica incorporan cabezales Gravotech en líneas de ensamblaje automatizadas donde el espacio disponible cuesta más de $2000/m² al año.
Eficiencia energética:
El consumo de energía nominal de 400 W (máximo 700 W), en comparación con los 1500-2000 W de sistemas comparables, reduce los requisitos de infraestructura eléctrica y las cargas de refrigeración. Esto es especialmente importante en la fabricación de salas blancas, donde los costes de HVAC dominan los gastos operativos.
Raymond Laser apunta a la fabricación de productos electrónicos de alto volumen y sensibles a los costos con sistemas de fibra, CO2 y UV con precios 25-40% inferiores a las alternativas europeas/japonesas, manteniendo al mismo tiempo un rendimiento aceptable para aplicaciones menos exigentes.
Especialización en Electrónica 3C:
La base de clientes de Raymond se concentra en los clústeres de fabricación de electrónica de Guangdong y el delta del río Yangtsé, donde se producen teléfonos inteligentes, tabletas, portátiles y wearables. Las instalaciones típicas producen entre 5000 y 8000 unidades por turno de 10 horas, un rendimiento adecuado para la electrónica de consumo, donde los requisitos de permanencia de la marca son menos estrictos que en las aplicaciones automotrices o médicas.
Integración en línea:
Los sistemas Raymond incorporan sincronización de transportadores, posicionamiento guiado por visión y conectividad con bases de datos que facilitan la automatización de la línea de producción. Un ensamblador de productos electrónicos que marcaba carcasas de aluminio para portátiles integró equipos Raymond en sus líneas SMT existentes, alcanzando una producción de 2400 marcas/hora.
Posición en el mercado:
Raymond compite principalmente por el costo de la inversión inicial, más que por la innovación técnica o el soporte integral. Los fabricantes que se sienten cómodos con las capacidades internas de desarrollo de procesos y mantenimiento consideran que los equipos Raymond ofrecen un retorno de la inversión aceptable para aplicaciones sencillas y de gran volumen. Sin embargo, las empresas que requieren ingeniería de aplicaciones exhaustiva, procesos validados o compromisos de servicio plurianuales suelen optar por proveedores occidentales o japoneses consolidados, a pesar de los mayores costos de adquisición.
El marcado de componentes automotrices se enfrenta a los requisitos de durabilidad más exigentes fuera del sector aeroespacial: las marcas deben permanecer legibles después de más de 15 años de exposición continua a la intemperie. La niebla salina, los ciclos térmicos, la contaminación por aceite, el lavado a alta presión y la abrasión mecánica degradan continuamente las características de la superficie.
Grabado profundo en bloques de motor de hierro fundido:
La serialización del VIN en bloques de motor de hierro fundido requiere un grabado de 0,3 a 0,5 mm de profundidad, lo que equilibra la permanencia con los riesgos de concentración de tensiones. Un fabricante de sistemas de propulsión descubrió que las marcas superficiales (0,15 mm) se volvían ilegibles tras 800 horas de exposición a niebla salina, mientras que una profundidad excesiva (>0,6 mm) creaba puntos de inicio de grietas por fatiga durante las pruebas de durabilidad.
El desarrollo del proceso identificó los parámetros óptimos: láser de fibra de 80 W, velocidad de escaneo de 1200 mm/s, frecuencia de 60 kHz, lo que produce una profundidad promedio de 0,38 mm con una variación de 0,04 mm. Tras 5000 horas de pruebas de corrosión acelerada, las marcas mantuvieron una legibilidad de Grado B (ISO/IEC 15415), cumpliendo con los requisitos del período de garantía con un margen considerable.
Recocido en acero inoxidable:
Las carcasas de los sensores automotrices (acero inoxidable 304) utilizan recocido láser, lo que crea marcas de óxido negro sin eliminar material. Esto preserva la resistencia a la corrosión, un factor crucial porque las marcas grabadas crean grietas que atrapan la humedad y favorecen la formación de picaduras.
Los parámetros requieren un control preciso: potencia promedio de 40 W, velocidad de escaneo de 800 mm/s, lo que genera una temperatura superficial máxima de 550-620 °C (medida con pirómetro). Las temperaturas superiores a 680 °C provocan la precipitación de carburo, lo que reduce la resistencia a la corrosión, mientras que un calentamiento insuficiente produce marcas grises con bajo contraste.
Las pruebas de campo validan este enfoque: las marcas recocidas sobreviven a una exposición de 3000 horas a la niebla salina sin degradarse, mientras que las marcas grabadas en material idéntico muestran corrosión por picaduras en 1200 horas.
Matriz de datos 2D sobre componentes de seguridad:
Los módulos de control de airbag, los sensores ABS y los componentes de la dirección requieren códigos Data Matrix 2D que resistan condiciones extremas y mantengan la legibilidad mecánica. La clasificación ISO/IEC 15415 Grado A (≥3,5/4,0) garantiza un escaneo fiable en condiciones de línea de producción.
Un fabricante de componentes de seguridad tenía problemas con la calidad de marcado inconsistente: los códigos variaban del Grado A al Grado D según el operador, el lote de material y la temperatura ambiente. La investigación reveló tres causas principales:
Las soluciones incluyeron la actualización a una fuente láser con estabilización de temperatura (estabilidad de potencia ±2%), la implementación de un enfoque automático motorizado (precisión de ±0,1 mm) y la incorporación de la limpieza automatizada de superficies (tratamiento con plasma). La capacidad del proceso resultante fue: Ppk = 1,67 (Grado A), con cero marcas de Grado C o D en una producción de 500.000 unidades.
El marcado UDI de dispositivos médicos aborda requisitos en competencia: identificación permanente que sobrevive a décadas de uso clínico versus preservación de la propiedad del material, garantizando la seguridad y eficacia del dispositivo.
Implantes ortopédicos de titanio:
El marcado láser de vástagos de cadera, componentes de rodilla e implantes espinales de aleación de titanio (Ti-6Al-4V) presenta desafíos únicos. Las marcas deben resistir más de 30 años de carga mecánica continua en entornos corrosivos con fluidos corporales sin generar concentración de tensiones ni corrosión por grietas que comprometan la longevidad del implante.
Investigación publicada en Revista de investigación de materiales biomédicos Las marcas recocidas por láser (que crean una fina capa de óxido sin eliminar material) mantienen una resistencia a la fatiga equivalente a la de los controles sin marcar. Por el contrario, las marcas grabadas (0,05 mm de profundidad) reducen la vida útil por fatiga 12-18% debido a la concentración de tensión en los bordes de la marca.
Un fabricante ortopédico validó el siguiente proceso:
La presentación 510(k) de la FDA incluyó pruebas de biocompatibilidad integrales según la norma ISO 10993:
Dispositivos médicos de polímeros: necesidad de láser UV:
Las jeringas de policarbonato, las jaulas espinales de PEEK y los componentes de unión de UHMWPE requieren marcado láser UV a una longitud de onda de 355 nm. Los láseres de fibra (1064 nm) generan un estrés térmico excesivo que provoca la propagación de microfisuras durante los ciclos de esterilización o la carga mecánica.
Un fabricante de dispositivos médicos especificó inicialmente un láser de fibra de 20 W para bandejas quirúrgicas de policarbonato, basándose en consideraciones de inversión. Durante la validación, las muestras no superaron la prueba de grietas por tensión ambiental: las microgrietas iniciadas en los límites de las marcas se propagaron durante la exposición a la esterilización con óxido de etileno. El reprocesamiento con láser UV eliminó las grietas por tensión y logró una legibilidad de código de Grado A.
Mecanismo físico: Los fotones de 355 nm poseen una energía de 3,5 eV (frente a los 1,2 eV de los de 1064 nm), suficiente para romper enlaces CC directamente mediante mecanismos fotoquímicos en lugar de térmicos. Las mediciones de la zona afectada por el calor (termografía infrarroja) muestran una penetración térmica de <15 μm frente a los >80 μm de los láseres de fibra.
Instrumentos quirúrgicos de acero inoxidable:
El instrumental quirúrgico reutilizable se somete a entre 100 y 500 ciclos de esterilización durante su vida útil. Las marcas láser deben resistir repetidas esterilizaciones en autoclave (134 °C, 3 bares de presión y detergentes de alto pH) sin degradarse.
La validación del proceso incluye:
Un fabricante de instrumentos validó los parámetros del láser de fibra de 50 W, produciendo caracteres grabados de 0,05 mm. Tras 250 ciclos de autoclave y pruebas con almohadilla abrasiva (que simulan la manipulación de un técnico quirúrgico), las marcas mantuvieron una legibilidad de Grado B. Cabe destacar que las pruebas mecánicas confirmaron que no se redujo la vida útil del instrumento, un factor crítico para fórceps, tijeras y pinzas sometidas a flexión repetida.
El marcado de placas de circuito FR-4 presenta un problema de optimización impulsado por restricciones: lograr códigos de alta resolución en sustratos sensibles a la temperatura sin delaminación, oxidación del cobre o degradación de la máscara de soldadura.
Requisitos técnicos del láser UV:
El compuesto de vidrio y epoxi FR-4 absorbe eficientemente la longitud de onda de 355 nm, mientras que la longitud de onda corta permite puntos de enfoque de 15 a 18 μm, esenciales para marcar códigos densos en superficies de PCB abarrotadas.
Un fabricante de teléfonos inteligentes marca códigos QR de 4 mm x 4 mm en placas base que contienen información para diagnósticos de servicio de campo. Los códigos deben sobrevivir:
Parámetros del proceso (láser UV de 5 W):
La termografía durante el marcado muestra una temperatura superficial máxima de 185 °C, muy por debajo de la transición vítrea FR-4 (170-180 °C), donde se produce el ablandamiento del polímero. La microscopía transversal confirma la ausencia de delaminación entre las capas de cobre y sustrato.
Optimización del contraste en la máscara de soldadura verde:
El marcado láser UV sobre máscara de soldadura verde produce marcas blancas mediante la degradación localizada del polímero. El contraste de la marca depende fundamentalmente de la fluencia del láser (energía por área).
El control de calidad de producción supervisa el contraste de las marcas mediante sistemas de visión que miden los valores de la escala de grises. La retroalimentación automática ajusta la potencia del láser manteniendo una relación de contraste de 85-92% a pesar de las variaciones en la máscara de soldadura entre lotes.
Los costos de adquisición de equipos representan entre 30 y 401 TP3T del costo total real de propiedad durante ciclos de vida de 10 años. Un análisis financiero exhaustivo debe considerar los gastos operativos, el impacto en la calidad y el valor estratégico.
Perfil de la empresa:
Evaluación de la inversión:
Selección del sistema: Láser de fibra de 50 W (MECCO SMARTmark) con fijación giratoria de dos posiciones
Cambios en los costos operativos anuales:
Impacto laboral:
Mejora de la calidad:
Mantenimiento:
Costos de energía:
Valor de flexibilidad:
Beneficio neto anual total: $194,480
Métricas financieras:
Beneficios estratégicos no cuantificados:
Complejidad de integración:
Muchos proveedores cotizan precios de equipos sin incluir los costos de integración, que representan entre 20 y 501 TP3T de la inversión total del proyecto:
Costos de oportunidad del tiempo de inactividad:
Los equipos de marcado críticos para la producción requieren un análisis de confiabilidad:
Una línea de envasado farmacéutico genera 2,4 millones de T/T de ingresos diarios (operación de tres turnos). Una falla en el sistema de marcado láser detiene la producción. Los sistemas premium (TRUMPF, Coherent) con contratos de servicio integrales alcanzan un tiempo de actividad de 981 T/T, frente a los 931 T/T de las alternativas económicas. La diferencia de 5 puntos porcentuales equivale a 43.000 T/T al año en pérdidas por tiempo de inactividad evitado, lo que justifica un aumento de 15.000 T/T en el coste de adquisición, además de un contrato de servicio anual de 8.000 T/T.
Formación y transferencia de conocimiento:
Los sistemas intuitivos (KEYENCE, FOBA) reducen los requisitos de capacitación de 40 a 8 horas, lo cual es significativo en entornos de fabricación con alta rotación de personal. Diferencia en el costo anual de capacitación: $12,000-$18,000 para instalaciones con un promedio de 3-4 cambios de operador al año.
La fabricación moderna exige que los sistemas de marcado láser funcionen como nodos de recopilación de datos dentro de fábricas inteligentes, no simplemente como dispositivos de identificación independientes.
El fabricante de productos electrónicos para automóviles implementó una trazabilidad integral que vincula la serialización a nivel de componentes a través del ensamblaje del vehículo:
Cuando surgieron fallas en el campo del controlador del airbag (posible llamada a revisión por seguridad que afectó a 2,3 millones de vehículos), la trazabilidad integral identificó las unidades afectadas en 3 horas. La causa se rastreó hasta el lote del proveedor del condensador enviado durante un período específico de dos semanas. La llamada a revisión quirúrgica se centró en 18.400 vehículos, frente a los 2,3 millones sin datos de serialización, lo que supuso un ahorro estimado de $340 millones en costos de llamada a revisión.
Los sistemas láser de primera calidad proporcionan una monitorización del proceso en tiempo real, lo que permite un control de calidad predictivo:
Parámetros monitoreados:
El fabricante farmacéutico implementó el monitoreo de SPC que desencadena acciones automatizadas:
Este monitoreo proactivo redujo el tiempo de inactividad no planificado del 67% (de 12 eventos/año a 4 eventos/año) al identificar los componentes degradados antes de que fallaran por completo.
El fabricante por contrato de dispositivos médicos integró el marcado láser con los sistemas empresariales creando una gestión de calidad de circuito cerrado:
Flujo del proceso:
Esta integración elimina errores de ingreso manual de datos (anteriormente 0,8% de envíos contenían discrepancias de serialización) al tiempo que proporciona un registro de auditoría completo que respalda los requisitos de inspección de la FDA.
Los sistemas láser avanzados permiten monitorear la vida útil de los componentes, lo que permite realizar reemplazos predictivos antes de que se produzcan fallas:
Monitoreo de componentes críticos:
La plataforma Oseon de TRUMPF demostró la optimización del mantenimiento en un fabricante con múltiples sitios:
Los acuerdos de servicio integrales parecen costosos (entre 10 y 151 TP3T de costo de equipo anualmente), pero el análisis revela valor para aplicaciones críticas de producción:
Comparación de contratos de servicios:
Enfoque Económico (Sin Contrato de Servicios):
Contrato de Servicio Integral:
Para equipos de producción que generan ingresos superiores a $3000/hora, el tiempo de actividad garantizado y los costos predecibles justifican contratos de servicio integrales. La reducción del tiempo de inactividad de 15 a 20 horas supone un ahorro de entre $45 000 y $60 000 en costos de oportunidad anuales.
Consideración crítica que a menudo se pasa por alto: ¿Qué sucede cuando un sistema láser de 8 años requiere un escáner galvanómetro reemplazado y ya no se fabrica?
Proveedores de nivel 1 (TRUMPF, Coherent, IPG): Mantenga la disponibilidad de piezas durante más de 15 años tras el cese de la producción. Los planos de ingeniería archivados permiten la fabricación a medida de componentes obsoletos.
Proveedores de nivel medio: Disponibilidad de piezas típica de 7 a 10 años. Tras la finalización del servicio, las reparaciones requieren recuperar componentes de unidades fuera de servicio o reemplazar el sistema completo.
Proveedores de la economía: Disponibilidad de piezas de 3 a 5 años. La rápida rotación de productos deja los sistemas antiguos prácticamente irreparables, lo que obliga a un reemplazo prematuro.
Un fabricante de dispositivos médicos descubrió esta diferencia de forma dolorosa: un sistema láser económico de seis años (costo original: 18.000 T/T) falló, lo que requirió el reemplazo del galvanómetro. Pieza no disponible, fabricante inactivo. Reemplazo de emergencia forzado (28.000 T/T + 12.000 T/T en costos de revalidación) durante un período crítico de producción. Costo total del incidente: 67.000 T/T, incluyendo la calificación acelerada del proveedor y la pérdida de producción.
Automoción/electrónica de alto volumen (entre 500.000 y 5 millones de unidades al año):
Requisitos: Máximo tiempo de actividad, tiempos de ciclo rápidos, verificación de calidad automatizada, mantenimiento predictivo
Proveedores recomendados: TRUMPF, Láser de Han, FOBA
Especificaciones clave: Láser de fibra de 50-100 W, verificación de visión integrada, contratos de servicio integrales
Rango de inversión: $80,000-$150,000 incluyendo automatización
ROI típico: 6-12 meses
Dispositivos médicos regulados por la FDA:
Requisitos: Procesos validados, documentación completa, biocompatibilidad, cumplimiento de la norma 21 CFR Parte 11
Proveedores recomendados: Coherente, TRUMPF, MECCO, FOBA
Especificaciones clave: Monitoreo de procesos, registro de auditoría, bibliotecas de parámetros validadas
Rango de inversión: $65,000-$120,000 incluyendo soporte de validación
ROI típico: 18-24 meses (más tiempo debido a los costos de validación, pero la mitigación de riesgos justifica la inversión)
Fabricación aeroespacial/defensa:
Requisitos: Cumplimiento de la norma MIL-STD-130N, trazabilidad del material, disponibilidad de piezas a largo plazo, sistemas de calidad AS9100D
Proveedores recomendados: MECCO, TRUMPF, Coherent, integradores basados en IPG
Especificaciones clave: Parámetros de aleación aeroespacial validados, documentación completa, capacidad de marcado UID
Rango de inversión: $55,000-$95,000 incluida la documentación de cumplimiento
ROI típico: 14-20 meses
Talleres de alta mezcla y fabricación por contrato:
Requisitos: Cambio rápido, complejidad de programación mínima, fijación flexible, amplia compatibilidad de materiales
Proveedores recomendados: KEYENCE, Gravotech, MECCO
Especificaciones clave: Interfaz de usuario intuitiva, posicionamiento guiado por visión, sistemas de enfoque automático
Rango de inversión: $35,000-$65,000
ROI típico: 10-16 meses
Aplicaciones especializadas multieje (geometrías complejas, materiales superduros):
Requisitos: Cinemática de 5 ejes, integración multiproceso, coordinación de mecanizado de precisión
Proveedores recomendados: Láser OPMT (plataformas especializadas)
Especificaciones clave: Funcionalidad RTCP, control de movimiento de grado CNC, capacidad de láser de femtosegundo
Rango de inversión: $120,000-$280,000
ROI típico: 16-28 meses (mayor recuperación de la inversión justificada por capacidades únicas que permiten nuevas aplicaciones)
Más allá de las especificaciones técnicas, estas preguntas revelan las capacidades de los proveedores:
Soporte de ingeniería de aplicaciones:
"¿Pueden proporcionar parámetros validados para la composición específica de nuestro material o tendremos que desarrollarlos internamente?" Los proveedores premium ofrecen amplias bibliotecas de materiales; los proveedores económicos esperan que los clientes se encarguen del desarrollo del proceso.
Documentación de validación:
¿Qué documentación de IQ/OQ/PQ proporciona para aplicaciones de dispositivos médicos/farmacéuticos? Los paquetes integrales ahorran de 8 a 12 semanas de tiempo de validación, lo que equivale a entre $40,000 y $80,000 en costos de ingeniería.
Garantías de respuesta del servicio:
¿Cuál es su plazo de respuesta contractual ante fallos que interrumpan la producción y qué sanciones económicas se aplican si no cumple con estos compromisos? Los proveedores que confían en la infraestructura de servicio ofrecen plazos de respuesta garantizados con sanciones económicas por fallos.
Disponibilidad de piezas a largo plazo:
"¿Cuánto tiempo garantiza la disponibilidad de piezas de repuesto después de la interrupción de la producción?" Los compromisos de más de 15 años indican que las empresas financieramente estables valoran las relaciones a largo plazo con los clientes.
Hoja de ruta tecnológica:
“¿Cómo se gestiona la obsolescencia cuando las computadoras de control o los protocolos de comunicación se vuelven obsoletos?” Los proveedores con visión de futuro ofrecen opciones de actualización; otros esperan la sustitución completa del sistema cada 7 a 10 años.
Mientras que los láseres de fibra de nanosegundos dominan el marcado industrial, los sistemas ultrarrápidos (duraciones de pulso <100 picosegundos) permiten aplicaciones que antes eran imposibles.
Diferencias en los mecanismos físicos:
Los pulsos de nanosegundos calientan el material, lo que provoca ablación térmica. La vaporización se produce mientras el material circundante permanece caliente, creando zonas afectadas por el calor. Los pulsos de picosegundos y femtosegundos suministran energía más rápidamente que las escalas de tiempo de difusión térmica. El material se vaporiza antes de que el calor se propague más allá del volumen focal inmediato, lo que genera una ablación fría con una ZAT inferior a 5 μm, frente a los 20-40 μm de los láseres de nanosegundos.
Ejemplos de aplicación:
Materiales transparentes: Los láseres de femtosegundos marcan volúmenes de vidrio en el interior mediante absorción no lineal, algo imposible con los sistemas de nanosegundos. Los fabricantes farmacéuticos marcan códigos de seguridad en el interior de los viales de vidrio, creando una identificación 3D inamovible sin destruir el envase.
Diamante y materiales superduros: Las plataformas láser de femtosegundos de OPMT procesan diamante CVD y carburo de silicio con un daño mínimo al subsuelo. Procesamiento láser de materiales ultraduros requiere un suministro preciso de energía que evite la propagación de grietas: los pulsos de femtosegundos logran esto mediante la formación de plasma confinado.
Eliminación de películas finas y recubrimientos: Los fabricantes de implantes médicos eliminan selectivamente los recubrimientos de nitruro de titanio de los instrumentos quirúrgicos mediante láseres de femtosegundos, lo que expone el metal base para la soldadura y preserva el recubrimiento en las superficies funcionales. Los sistemas de nanosegundos delaminan las áreas adyacentes mediante estrés térmico.
Limitaciones actuales: Las fuentes láser ultrarrápidas cuestan entre 3 y 5 veces más que sus equivalentes de nanosegundos, con una potencia promedio menor (10-50 W típicos frente a 100-200 W para nanosegundos). Las aplicaciones que requieren el máximo rendimiento siguen estando dominadas por la tecnología de nanosegundos.
Los algoritmos de aprendizaje automático optimizan los procesos de marcado láser más rápido que los ingenieros humanos y al mismo tiempo detectan problemas de calidad invisibles para la inspección convencional:
Optimización de parámetros:
Un proveedor automotriz implementó la optimización de parámetros basada en IA para el marcado de 47 aleaciones de aluminio diferentes (el contenido variable de silicio afecta las características de absorción). El enfoque tradicional requería de 4 a 6 horas de pruebas metalúrgicas por aleación para desarrollar los parámetros. El sistema de IA analizó más de 2000 marcas históricas, identificó correlaciones de coeficientes de absorción y generó parámetros validados en 15 minutos, lo que redujo el tiempo de calificación de nuevas aleaciones de 2 semanas a 2 días.
Monitoreo predictivo de la calidad:
El sistema de visión captura cada marca con una resolución de 20 megapíxeles. Las redes neuronales convolucionales, entrenadas con más de 500.000 imágenes, detectan patrones sutiles de degradación de la calidad y predicen fallos antes de que surjan defectos visibles para el ojo humano. El sistema identifica el desgaste de los rodamientos del galvanómetro entre 200 y 300 horas de funcionamiento antes de que la monitorización convencional active el mantenimiento, lo que evita entre 6 y 8 paradas de producción al año.
Control de procesos adaptativo:
La monitorización en tiempo real ajusta los parámetros del láser, compensando las variaciones del material, los cambios ambientales y el envejecimiento de los componentes. El fabricante de dispositivos médicos procesa titanio de tres proveedores con una variación del coeficiente de absorción de 8-12%. El sistema adaptativo mantiene una calidad de marca constante sin intervención del operador; anteriormente, se requería el ajuste manual de parámetros para cada lote del proveedor.
La tecnología emergente utiliza el chorro de agua como guía de ondas flexible que suministra energía láser, combinando la precisión de corte de los láseres con el enfriamiento de los chorros de agua.
Los sistemas guiados por agua permiten marcar sustratos sensibles al calor que son imposibles con los métodos convencionales: marcar dispositivos electrónicos mientras están ensamblados (el agua evita daños térmicos a los componentes adyacentes), procesar explosivos (el chorro de agua evita la ignición) y cortar materiales compuestos sin delaminación.
La adopción actual se limita a aplicaciones especializadas debido a su complejidad y coste (inversiones en sistemas de $200,000 a $400,000). Sin embargo, la fabricación de compuestos aeroespaciales muestra un creciente interés en el marcado de estructuras de fibra de carbono donde el calor láser convencional causa degradación de la matriz.
El aprendizaje de las implementaciones fallidas de marcado láser revela factores críticos de éxito:
Situación: El fabricante de implantes ortopédicos seleccionó el sistema láser económico ($32,000) basándose principalmente en el precio de adquisición. Las calificaciones iniciales resultaron aceptables durante las pruebas de aceptación.
Problemas surgidos:
Costo total de falla:
Lecciones clave:
Situación: Un proveedor de primer nivel adquirió un excelente sistema láser (TRUMPF TruMark) pero subestimó la complejidad de su integración en la línea de producción existente.
Desafíos de la integración:
Impacto en la línea de tiempo:
Lecciones clave:
Situación: El fabricante de teléfonos inteligentes especificó el láser UV para el marcado de PCB basándose en la exitosa implementación de la competencia. No se verificó la compatibilidad con la formulación específica de su máscara de soldadura.
Problema: El marcado láser UV produjo un contraste visual aceptable, pero el análisis químico reveló degradación del polímero de la máscara de soldadura. Las pruebas de envejecimiento acelerado (85 °C/85% RH, 1000 horas) mostraron que las regiones marcadas presentaban microfisuras que permitían la entrada de humedad, lo que ponía en peligro la fiabilidad a largo plazo.
Causa principal: El proveedor de máscaras de soldadura cambió su formulación (mejoró la resistencia al rayado) sin notificar a los clientes. La nueva formulación contenía aditivos que reaccionaban negativamente con la exposición al láser UV.
Solución: Se requirió un rediseño completo de los parámetros en colaboración con el proveedor de la máscara de soldadura. Se aprobó una formulación alternativa para marcado láser, pero se requirió la recalificación del proveedor de PCB, lo que amplió el plazo de lanzamiento del producto en seis semanas.
Lecciones clave:
La selección del equipo de marcado láser óptimo trasciende la comparación de especificaciones técnicas: requiere una evaluación integral de las capacidades del proveedor, el costo total de propiedad y la alineación con las prioridades operativas.
Para fabricantes conscientes de los costes en producciones estables y de gran volumen: Las plataformas láser de fibra consolidadas de Han's Laser, Raymond Laser o Gravotech ofrecen un rendimiento comprobado a precios competitivos. Estos sistemas destacan cuando las aplicaciones son sencillas, los materiales están bien caracterizados y se dispone de recursos de ingeniería internos para la optimización de procesos.
Para las industrias reguladas que priorizan el cumplimiento y la mitigación de riesgos: Proveedores premium como TRUMPF, Coherent, MECCO y FOBA ofrecen un soporte integral de validación, documentación exhaustiva e infraestructura de servicio que justifican los sobrecostos del 30-50%. Los fabricantes de dispositivos médicos y aeroespaciales constatan sistemáticamente que esta inversión reduce los costos totales del programa gracias a una calificación más rápida y un cumplimiento continuo.
Para una fabricación de alta variedad que requiere flexibilidad operativa: Las plataformas fáciles de usar y el posicionamiento guiado por visión de KEYENCE eliminan la complejidad de programación, lo que permite cambios rápidos: ventajas fundamentales en talleres y entornos de fabricación por contrato donde la utilización del equipo depende de minimizar el tiempo de configuración.
Para aplicaciones especializadas que involucran geometrías complejas o materiales avanzados: Las plataformas CNC multieje de OPMT Laser integran el marcado con el mecanizado de precisión y el procesamiento de superficies, lo que permite la producción completa de piezas en configuraciones únicas. Estos sistemas son ideales para fabricantes que requieren capacidades que no están disponibles en los equipos de marcado convencionales de 2 ejes.
La decisión de invertir en marcado láser equilibra, en última instancia, tres factores: la inversión inicial de capital, la rentabilidad operativa durante la vida útil del equipo y el valor estratégico mediante una mejor trazabilidad, la mejora de la calidad y la flexibilidad del proceso. Los entornos de fabricación que generan más de $2,000 ingresos por hora encuentran constantemente que los sistemas premium con un servicio técnico integral ofrecen un valor total superior a pesar de los mayores costos de adquisición.
Lo más importante: Involucre a los equipos de ingeniería de aplicaciones de los proveedores desde el principio del proceso de evaluación. Las instalaciones exitosas implican invariablemente una estrecha colaboración que implica desarrollar parámetros validados, realizar pruebas con materiales de producción reales y planificar una integración integral. La relación con su proveedor de equipos es tan importante como las especificaciones técnicas: elija socios que demuestren compromiso con el éxito a largo plazo del cliente en lugar de centrarse únicamente en el valor inicial de la transacción.
Acerca del láser OPMT (Tecnología Inteligente de Punto Original de Guangdong):
OPMT Laser se especializa en sistemas avanzados de procesamiento láser CNC multieje para la fabricación de precisión. Con 302 patentes concedidas, certificaciones ISO 9001/14001/45001 y una planta de fabricación de 50.000 m², OPMT ofrece soluciones innovadoras de mecanizado láser a las industrias automotriz, de herramientas y de dispositivos médicos en todo el mundo. Nuestros centros de mecanizado láser de 5 ejes de la serie Light 5X integran marcado, corte, texturizado y medición de precisión en plataformas unificadas, lo que permite un procesamiento completo de las piezas, eliminando configuraciones intermedias y mejorando la precisión geométrica.
Contacte con nuestro equipo de ingeniería de aplicaciones Para analizar sus necesidades de marcado de precisión y explorar cómo la tecnología láser multieje puede mejorar sus capacidades de fabricación: www.opmtlaser.com
Recursos técnicos relacionados:
Descargo de responsabilidad
Este contenido es compilado por OPMT Laser con base en información pública disponible únicamente como referencia; las menciones de marcas y productos de terceros son para comparación objetiva y no implican ninguna asociación o respaldo comercial.
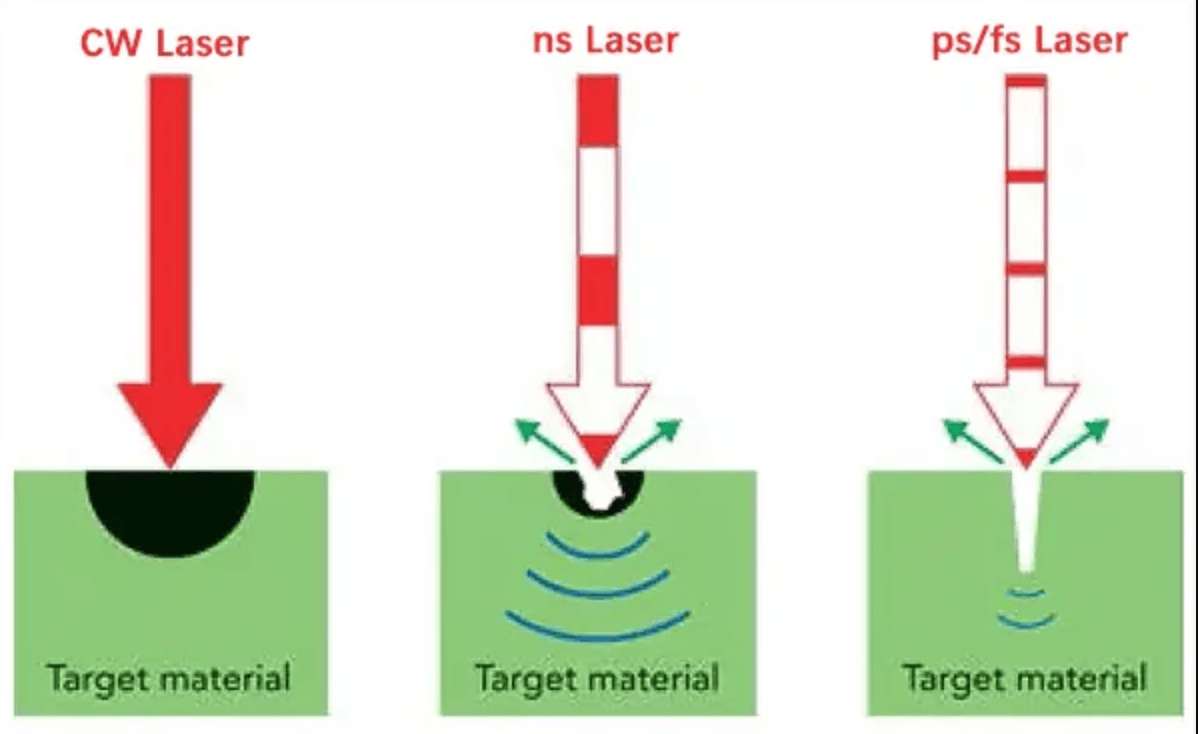
Compare sistemas láser de picosegundos y nanosegundos para la fabricación industrial. Datos de la ZAT, velocidades de procesamiento, análisis de costos y criterios de aplicación de los sistemas implementados por OPMT.

Las máquinas de corte láser PCD ofrecen una precisión de 0,003 mm y un procesamiento tres veces más rápido que la electroerosión. Guía técnica completa para la fabricación de herramientas de diamante policristalino para las industrias aeroespacial y automotriz.
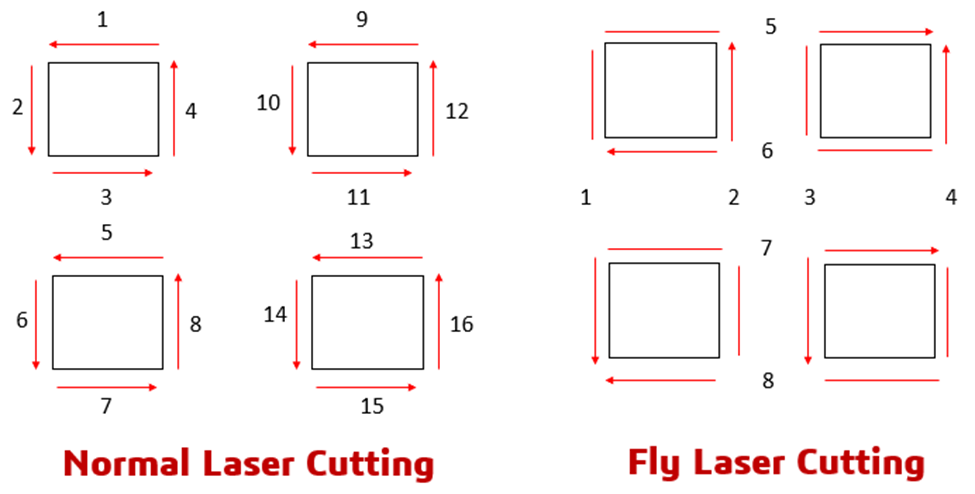
La tecnología láser de corte al vuelo reduce el tiempo de ciclo en un 30-50% mediante la optimización continua de la trayectoria de movimiento. Aprenda la mecánica, las aplicaciones y las especificaciones de los equipos OPMT para la fabricación de precisión.

Marcos de evaluación de fábricas para la adquisición de equipos de corte láser. Evaluación de infraestructura, análisis de sistemas de calidad y cálculo del coste total de propiedad (CTP) basado en más de 30 auditorías de instalaciones.
Por favor, rellene sus datos de contacto para descargar el PDF.

